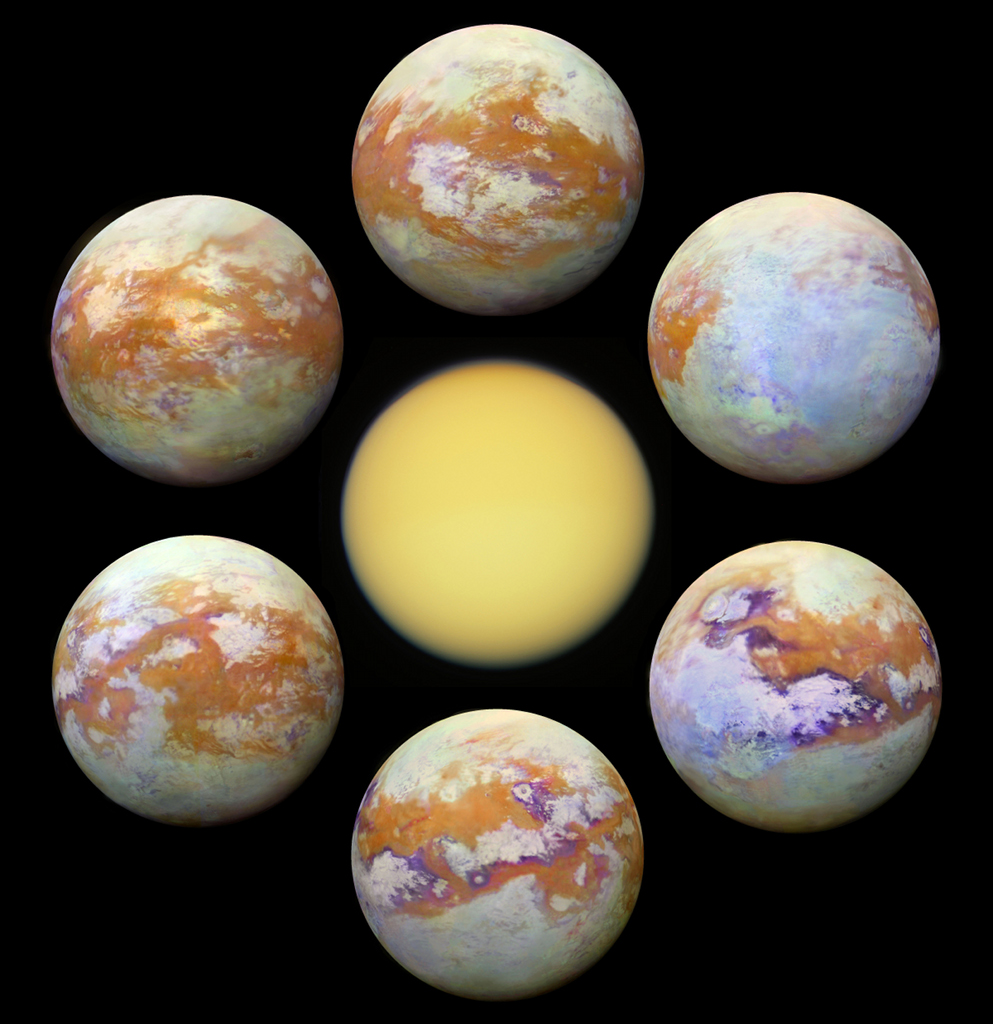
天市右垣十一: 速逃星
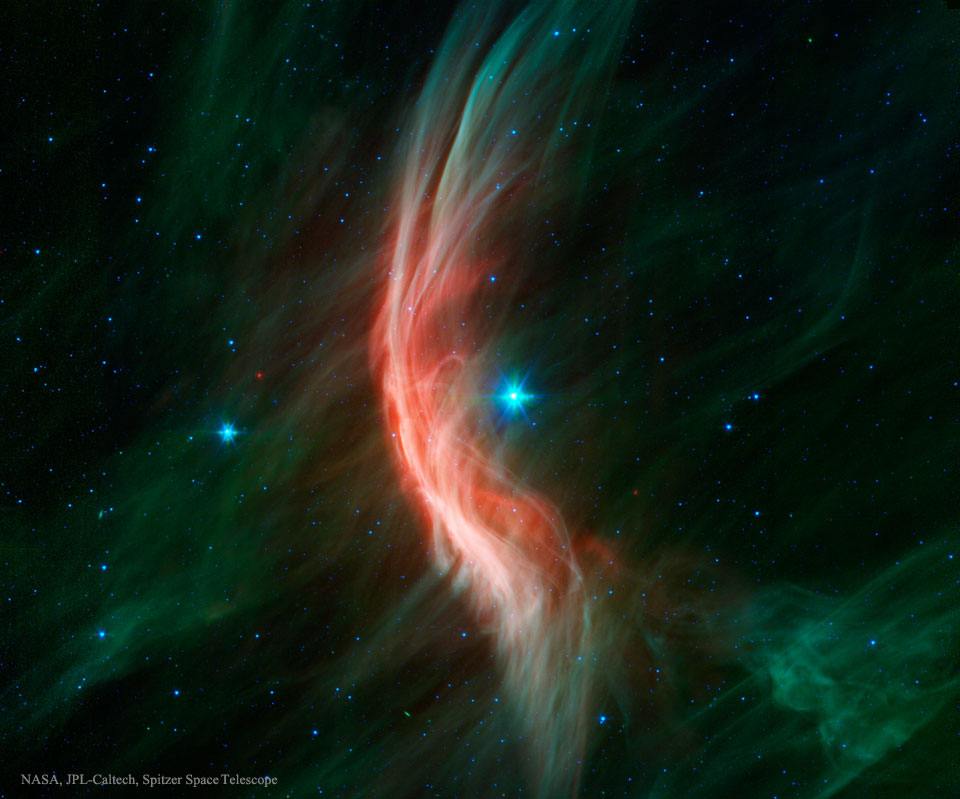
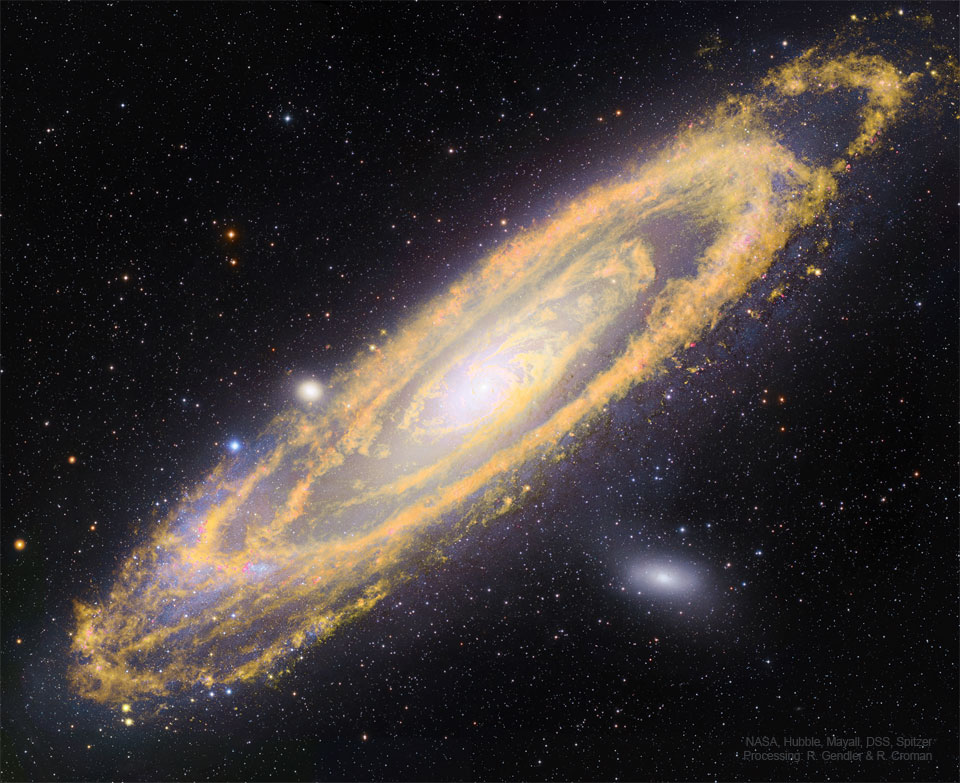
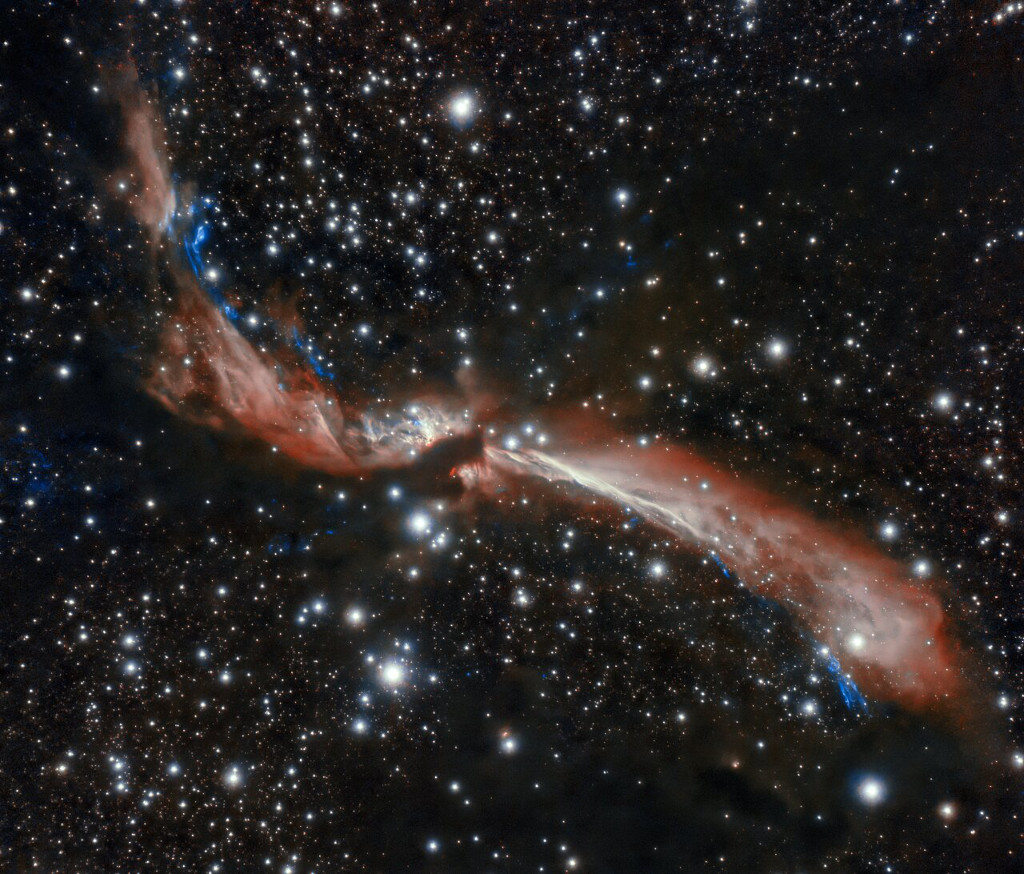
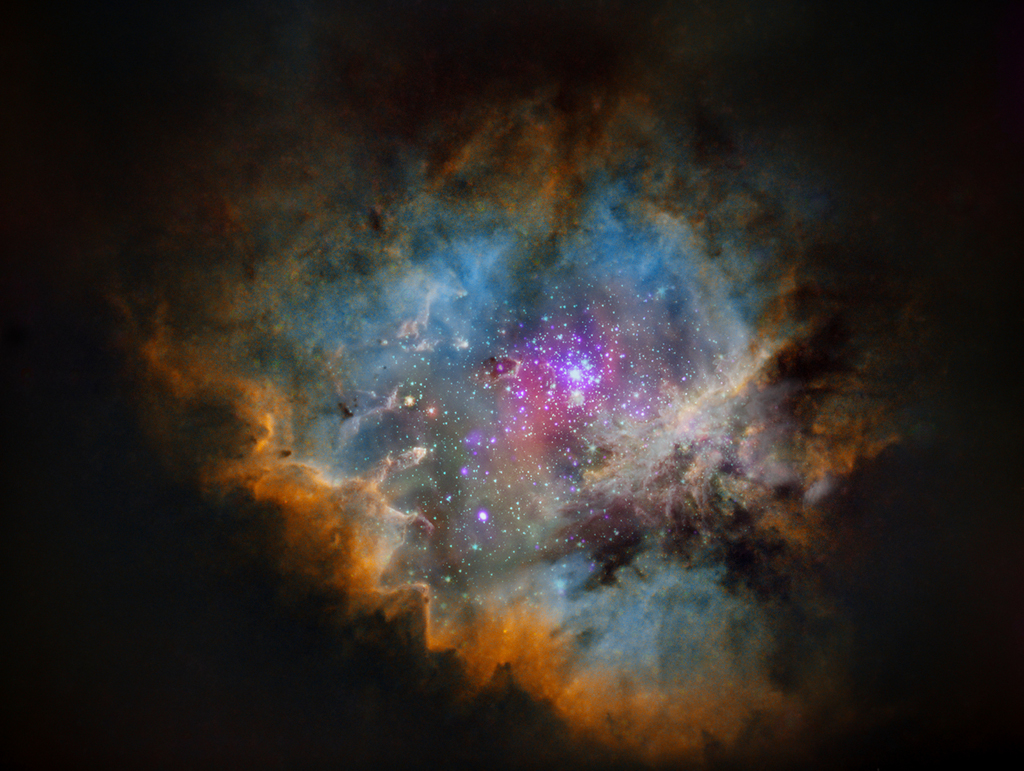
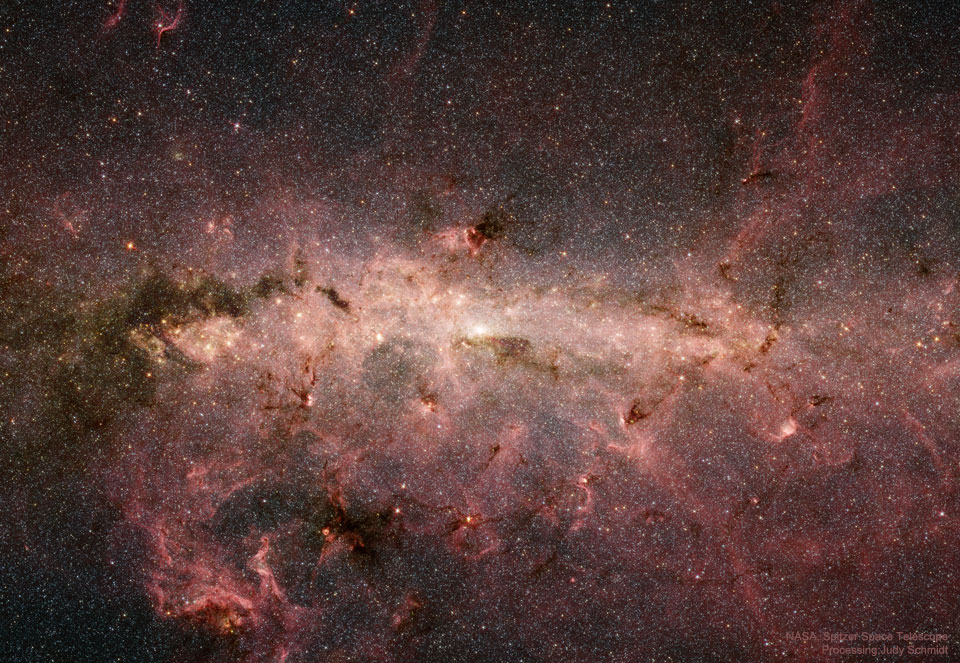
2024年1月4日 Zeta Oph: Runaway Star Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Spitzer Space Telescope Explanation: Like a ship plowing through cosmic seas, runaway star Zeta Ophiuchi produces the arcing interstellar bow wave or bow shock seen in this stunning infrared portrait. In the false-color view, bluish Z […]