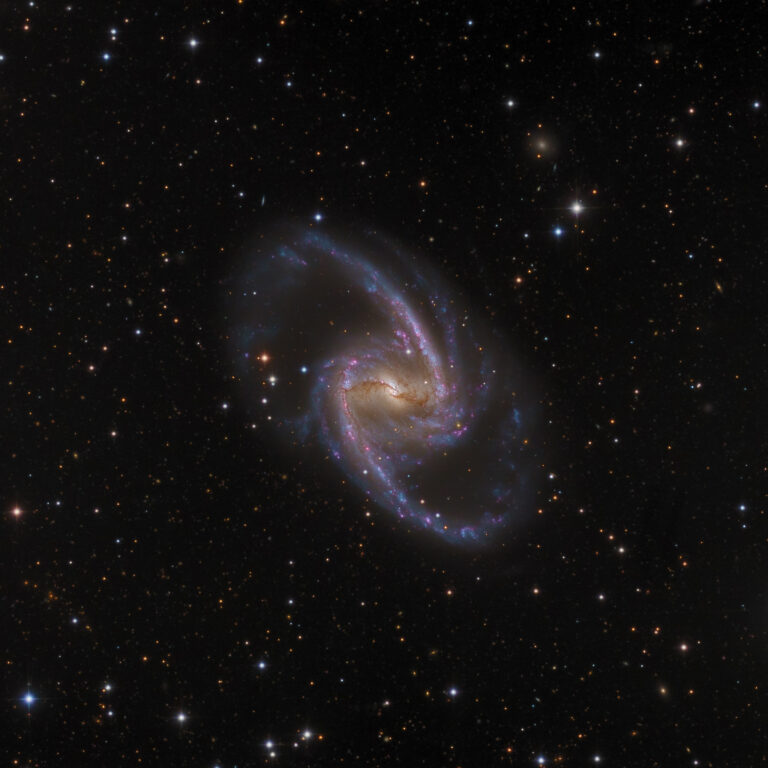
NGC 1365: 壮丽的宇宙岛
2021年01月08日 NGC 1365: Majestic Island Universe Image Credit & Copyright: Mike Selby, Leonardo Orazi Explanation: Barred spiral galaxy NGC 1365 is truly a majestic island universe some 200,000 light-years across. Located a mere 60 million light-years away toward the chemical constellation Fornax, NGC 1365 is a dominant member of the well-studied Fornax Cluster of galaxies. This impressively sharp color image shows the intense, reddish star forming regions near the ends of central bar and along the spiral arms, with details of the obscuring dust lanes cutting across the galaxy’s bright core. At the core lies a supermassive black hole. Astronomers think NGC 1365’s prominent bar plays a crucial role in the galaxy’s evolution, drawing gas and dust into a star-forming maelstrom and ultimately feeding material…