朱诺号影像: 木卫三
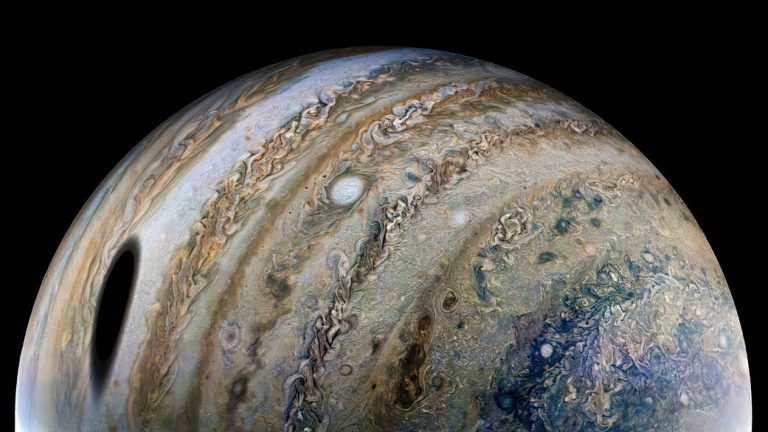
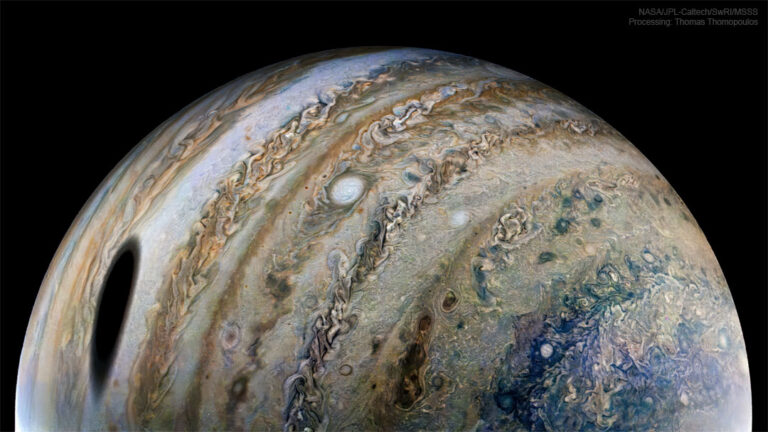
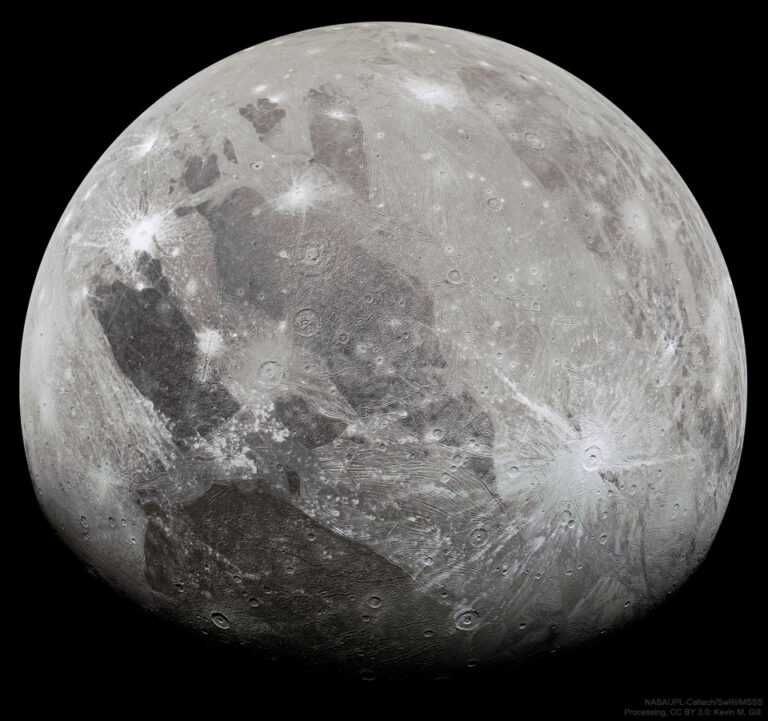
2023年11月28日 Ganymede from Juno Image Credit & Copyright: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS; Processing & License: Kevin M. Gill; Explanation: What does the largest moon in the Solar System look like? Jupiter‘s moon Ganymede, larger than even Mercury and Pluto, has an icy surface speckled with bright young craters overlying a mixture of older, darker, more cratered terrain laced with grooves and ridges. The cause of the grooved terrain remains a topic of research, with a leading hypothesis relating it to shifting ice plates. Ganymede is thought to have an ocean layer that contains more water than Earth — and might contain life. Like Earth’s Moon, Ganymede keeps the same face towards its central planet, in this case Jupiter. The featured image was captured in 2021 by NASA’s robotic…