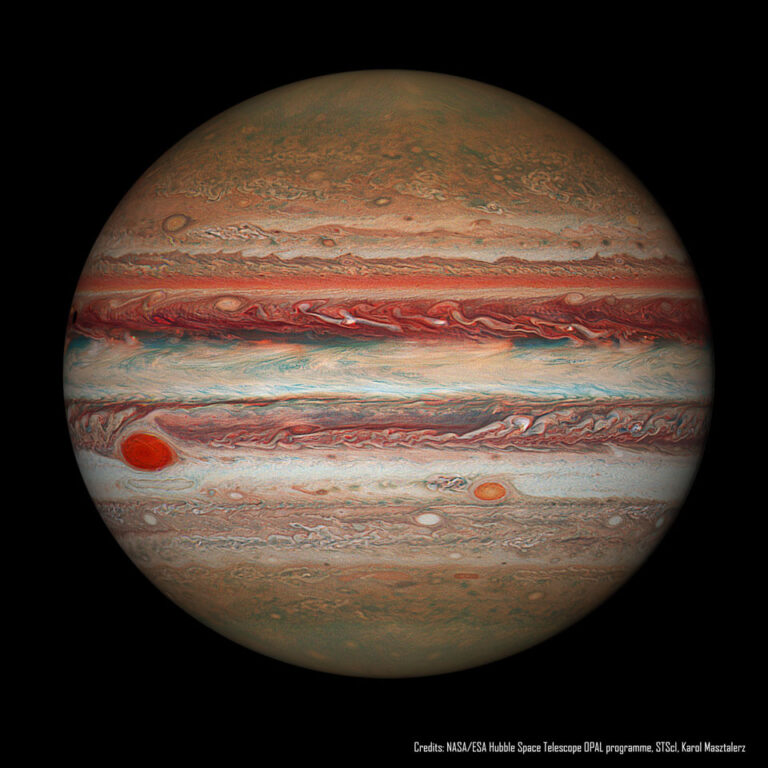
哈勃望远镜的木星和缩小的大红斑
2022年1月9日 Hubble’s Jupiter and the Shrinking Great Red Spot Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, OPAL Program, STScI; Processing: Karol Masztalerz Explanation: What will become of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? Gas giant Jupiter is the solar system’s largest world with about 320 times the mass of planet Earth. Jupiter is home to one of the largest and longest lasting storm systems known, the Great Red Spot (GRS), visible to the left. The GRS is so large it could swallow Earth, although it has been shrinking. Comparison with historical notes indicate that the storm spans only about one third of the exposed surface area it had 150 years ago. NASA’s Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program has been monitoring the storm more recently using the Hubble Space…