飞机凝结尾的X形影子
两架飞机的飞机凝结尾,交叉成一个X,显示在图像的中间。它们在深蓝色背景下呈亮白色。在阳光照耀下的飞机凝结尾上方,可以看到高高的云层。低处的太阳在高处的云层上形成了一个黑影。一排建筑物横跨图像的下部。有关更多详细信息,请参阅说明。
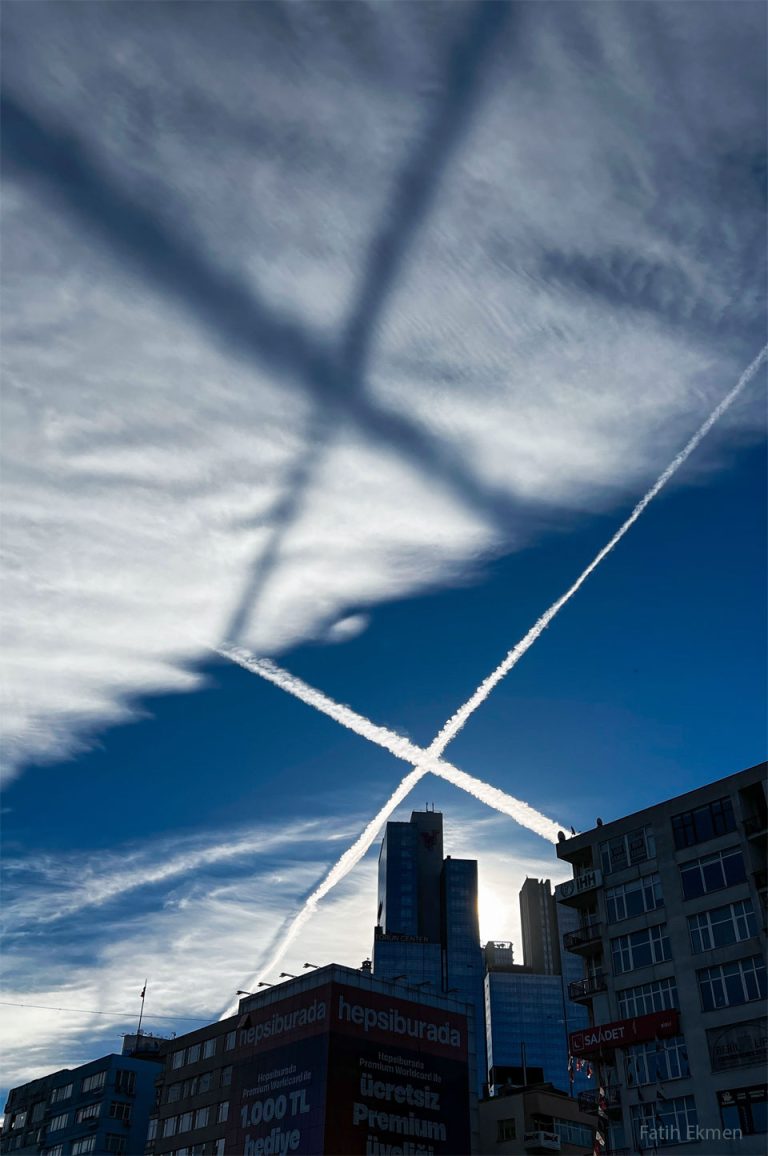

两架飞机的飞机凝结尾,交叉成一个X,显示在图像的中间。它们在深蓝色背景下呈亮白色。在阳光照耀下的飞机凝结尾上方,可以看到高高的云层。低处的太阳在高处的云层上形成了一个黑影。一排建筑物横跨图像的下部。有关更多详细信息,请参阅说明。
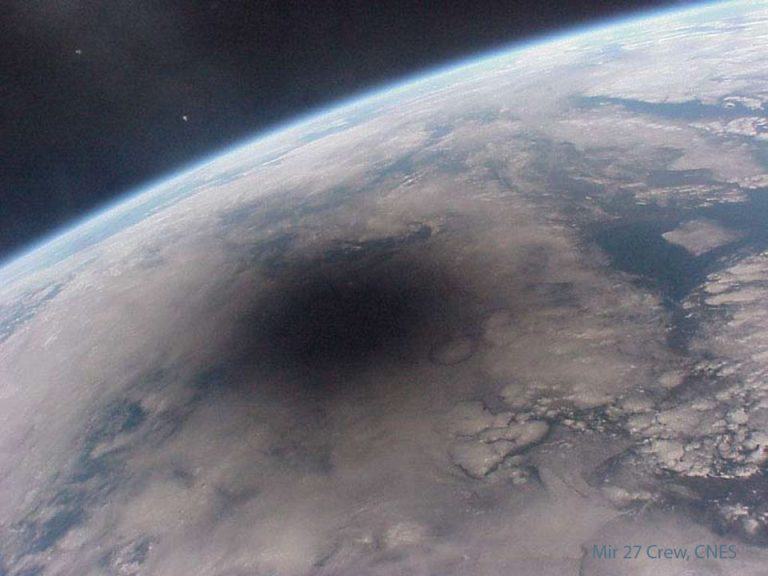

地球的一部分被蓝色的海洋和白色的云所描绘。左上角是深空黑暗背景。地球上有一个明显的大黑点。有关更多详细信息,请参阅说明。

2024年2月11日 Rocket Plume Shadow Points to the Moon Image Credit: Pat McCracken, NASA Explanation: Why would the shadow of a rocket’s launch plume point toward the Moon? In early 2001 during a launch of the space shuttle Atlantis, the Sun, Earth, Moon, and rocket were all properly aligned for this photogenic coincidence. First, for the space shuttle‘s plume to cast a long shadow, the time of day must be either near sunrise or sunset. Only then will the shadow be its longest and extend all the way to the horizon. Finally, during a Full Moon, the Sun and Moon are on opposite sides of the sky. Just after sunset, for example, the Sun is slightly below the horizon, and, in the other direction, the Moon…
2024年1月22日 Shadows of Mountain and Moon Image Credit & Copyright: Enzo Massa Micon Explanation: Can the Moon and a mountain really cast similar shadows? Yes, but the division between light and dark does not have to be aligned. Pictured, a quarter moon was captured above the mountain Grivola in Italy in early October of 2022. The Sun is to the right of the featured picturesque landscape, illuminating the right side of the Moon in a similar way that it illuminates the right side of the mountain. This lunar phase is called “quarter” because the lit fraction visible from Earth is one quarter of the entire lunar surface. Digital post-processing of this single exposure gave both gigantic objects more prominence. Capturing the terminator of this quarter…
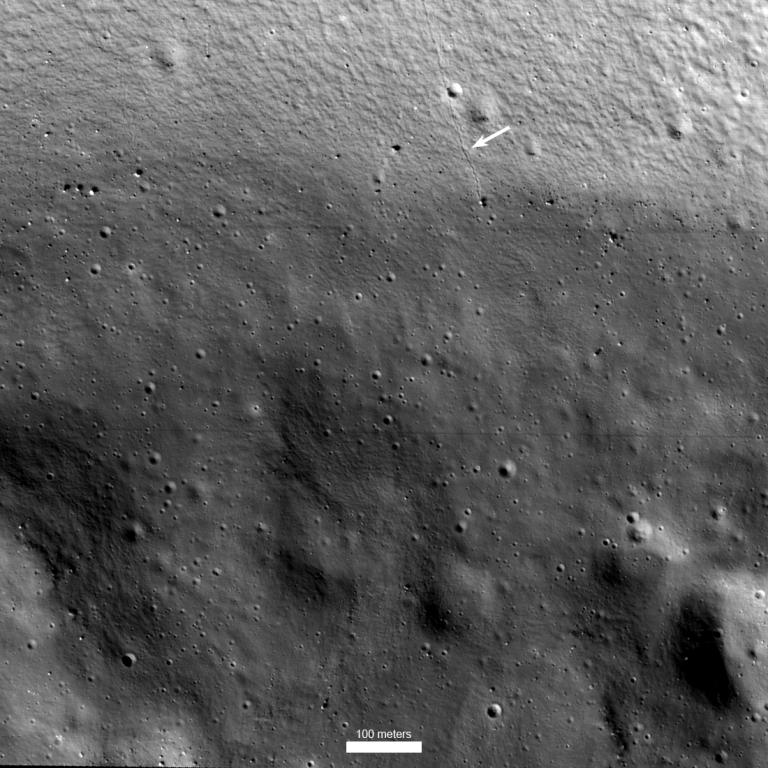

2023年5月5日 Shackleton from ShadowCam Image Credit: NASA, ShadowCam, Korea Aerospace Research Institute, Arizona State University Explanation: Shackleton crater lies at the lunar south pole. Peaks along the 21 kilometer diameter are in sunlight, but Shackleton’s floor is in dark permanent shadow. Still, this image of the shadowed rim wall and floor of Shackleton crater was captured from NASA’s ShadowCam, an instrument on board the Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter (KPLO) launched in August 2022. About 200 times more sensitive than, for example, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter’s Narrow Angle Camera, ShadowCam was designed image the permanently shadowed regions of the lunar surface. Avoiding direct sunlight, those regions are expected to be reservoirs of water-ice and other volatiles deposited by ancient cometary impacts and useful to future Moon…
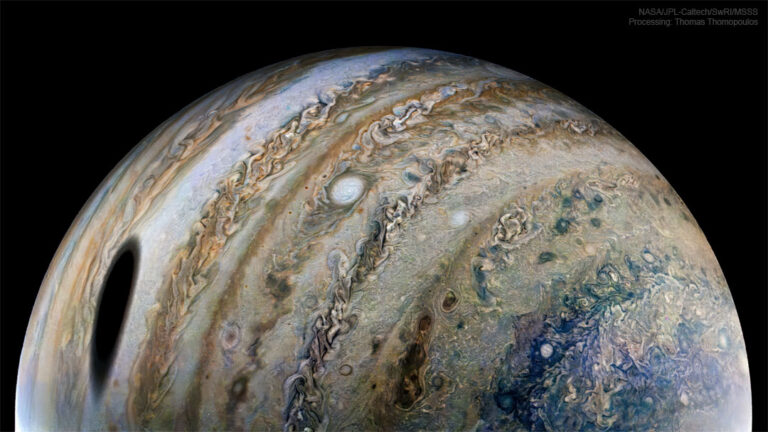

2022年4月27日 Moon Shadow on Jupiter Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS; Processing & License: Thomas Thomopoulos Explanation: What is that large dark spot on Jupiter? It’s the shadow of Ganymede, Jupiter’s largest moon. When Jupiter’s moons cross between the Jovian giant and the Sun, they created shadows just like when the Earth’s moon crosses between the Earth and the Sun. Also like on Earth, if you were in a dark shadow on Jupiter, you would see a moon completely eclipse the Sun. Unlike on Earth, moon shadows occur most days on Jupiter — what’s more unusual is that a spacecraft was close enough to record one with a high-resolution image. That spacecraft, Juno, was passing so close to Jupiter in late February that nearby clouds and the dark…
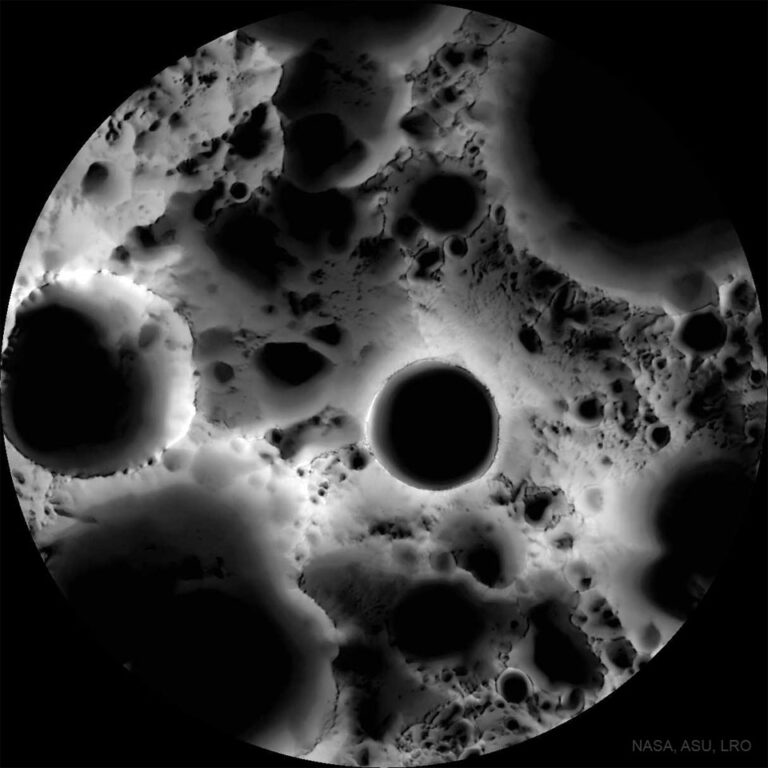
2022年4月10日 Shadows at the Moon’s South Pole Image Credit: NASA, Arizona State U., Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Explanation: Was this image of the Moon’s surface taken with a microscope? No — it’s a multi-temporal illumination map made with a wide-angle camera. To create it, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft collected 1,700 images over a period of 6 lunar days (6 Earth months), repeatedly covering an area centered on the Moon’s south pole from different angles. The resulting images were stacked to produce the featured map — representing the percentage of time each spot on the surface was illuminated by the Sun. Remaining convincingly in shadow, the floor of the 19-kilometer diameter Shackleton crater is seen near the map’s center. The lunar south pole itself is at…
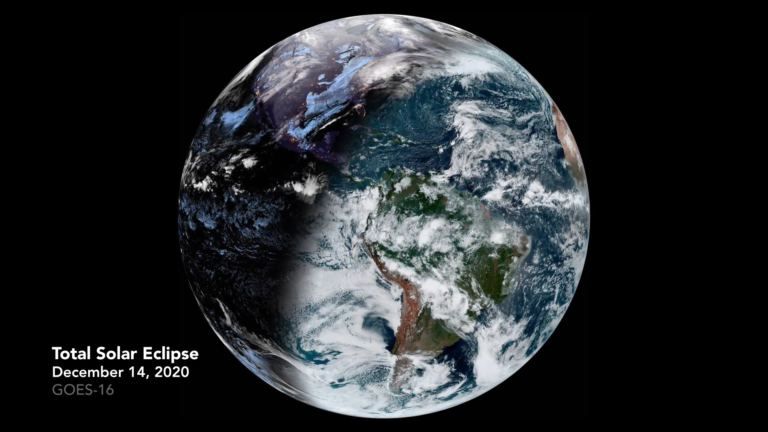

2020年12月29日 Earth During a Total Solar Eclipse Video Credit: GOES-16, ABI, NOAA, NASA Explanation: What does the Earth look like during a total solar eclipse? It appears dark in the region where people see the eclipse, because that’s where the shadow of the Moon falls. The shadow spot rapidly shoots across the Earth at nearly 2,000 kilometers per hour, darkening locations in its path — typically for only a few minutes — before moving on. The featured video shows the Earth during the total solar eclipse earlier this month. The time-lapse sequence, taken from a geostationary satellite, starts with the Earth below showing night but the sun soon rises at the lower right. Clouds shift as day breaks over the blue planet. Suddenly the circular…