2020年7月5日
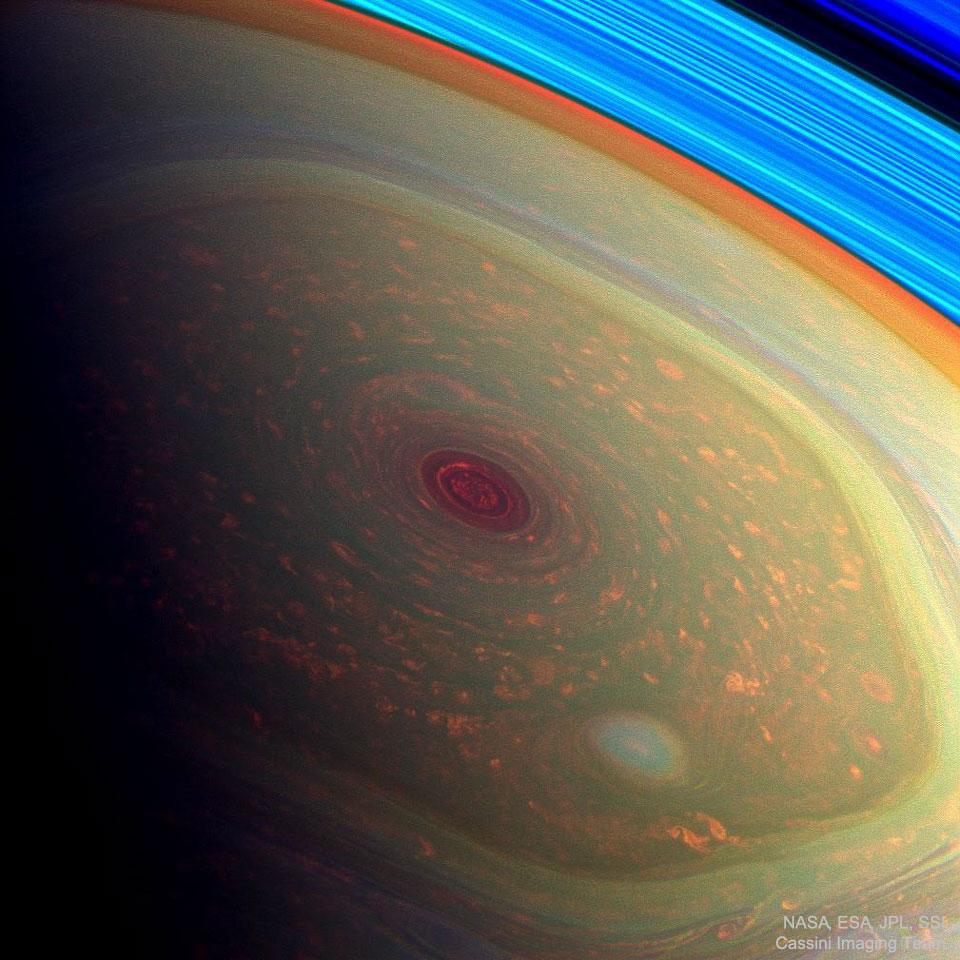
Saturn’s Northern Hexagon
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, JPL, SSI, Cassini Imaging Team
Explanation: Why would clouds form a hexagon on Saturn? Nobody is sure. Originally discovered during the Voyager flybys of Saturn in the 1980s, nobody has ever seen anything like it anywhere else in the Solar System. Acquiring its first sunlit views of far northern Saturn in late 2012, the Cassini spacecraft’s wide-angle camera recorded this stunning, false-color image of the ringed planet’s north pole. The composite of near-infrared image data results in red hues for low clouds and green for high ones, giving the Saturnian cloudscape a vivid appearance. This and similar images show the stability of the hexagon even 20+ years after Voyager. Movies of Saturn’s North Pole show the cloud structure maintaining its hexagonal structure while rotating. Unlike individual clouds appearing like a hexagon on Earth, the Saturn cloud pattern appears to have six well defined sides of nearly equal length. Four Earths could fit inside the hexagon. Beyond the cloud tops at the upper right, arcs of the planet’s eye-catching rings appear bright blue.
Tomorrow’s picture: deep hunter
土星的北极六角云
影像提供: NASA, ESA, JPL, SSI, Cassini Imaging Team
说明: 为何土星的云形会如六角?目前没人知道其成因。它是在1980年代航行者号掠过土星时,首次发现的,在那之前,太阳系内从来没见过这样的系统。后来在2012年底,卡西尼号太空船的广视角相机在土星日曜的北极区,拍下了这幅土星极区的精采假色影像。在这张由近红光数据组合成的影像里,以红色标示低层云,绿色标示高层层,让土星的云景变得格外鲜活。这幅及其他的影像,证实自航行者号发现后,这个六角云已稳定存在了20年以上。土星北极区的影片也证实,这种云在回旋时仍然维持六角结构。此外,和地球上形如六角的云不同,土星的这种云形有6个等长的鲜明边界,而且六角形之内可容纳4个地球。在右上方的云顶后方,可见到渲染成亮蓝色的土星环弧。
明日的图片: deep hunter