2021年04月15日
The Galaxy, the Jet, and a Famous Black Hole
Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration
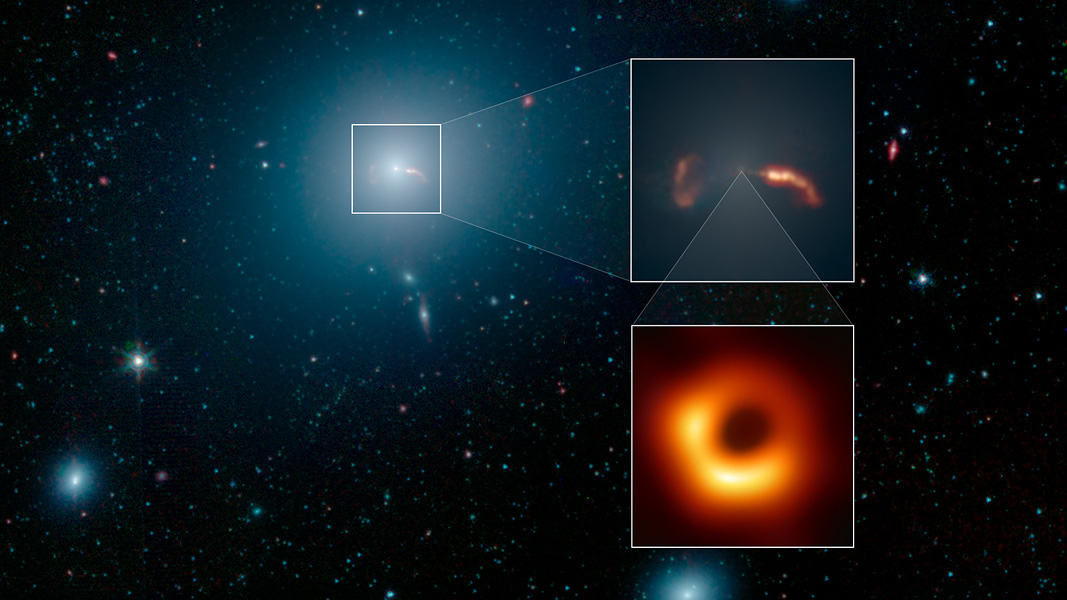
Explanation: Bright elliptical galaxy Messier 87 (M87) is home to the supermassive black hole captured by planet Earth’s Event Horizon Telescope in the first ever image of a black hole. Giant of the Virgo galaxy cluster about 55 million light-years away, M87 is the large galaxy rendered in blue hues in this infrared image from the Spitzer Space telescope. Though M87 appears mostly featureless and cloud-like, the Spitzer image does record details of relativistic jets blasting from the galaxy’s central region. Shown in the inset at top right, the jets themselves span thousands of light-years. The brighter jet seen on the right is approaching and close to our line of sight. Opposite, the shock created by the otherwise unseen receding jet lights up a fainter arc of material. Inset at bottom right, the historic black hole image is shown in context, at the center of giant galaxy and relativistic jets. Completely unresolved in the Spitzer image, the supermassive black hole surrounded by infalling material is the source of enormous energy driving the relativistic jets from the center of active galaxy M87.
Tomorrow’s picture: pixels on the horizon
星系M87、喷流与著名黑洞
影像提供: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration
说明: 明亮椭圆星系M87内的超大质量黑洞,是地面事件视界望远镜拍摄的首张黑洞照片之标的。在这张史匹哲太空望远镜红外光影像里的泛蓝天体,即是室女室星系团里,庞大无比、距离约5千5百万光年远的M87。虽然M87乍看之下,形似一个没有太多特征的云团,然而史匹哲影像还是能解析出,从这个星系中心区喷出的相对论性喷流。星系右侧较明亮的喷流,非常接近我们的视线。而其左侧基本不可见的远去喷流,则冲撞激震物质产并生一道暗淡的光弧。影像右下的嵌图,则是文中提到的历史性黑洞影像,影像并显示了黑洞与这个庞大星系的核心及相对论性喷流之相对关系。在史匹哲影像完全无法分辨的,还有环拱在超大质量黑洞周围的内坠物质,然而它们却是驱动相对论性喷流,从活跃星系M87的核心喷出之庞大能源。
明日的图片: pixels on the horizon