2022年10月17日
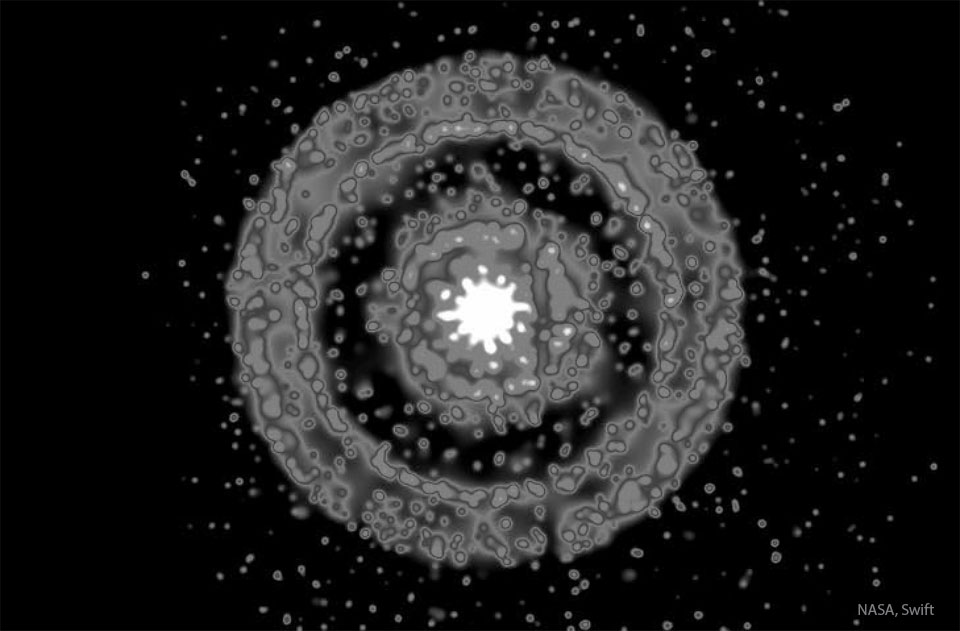
X-Ray Rings Around a Gamma Ray Burst
Image Credit: NASA Swift Obs.; Data: B. Cenko (NASA’s GSFC), A. Beardmore (U. Leicester) et al.; Processing: J. Miller (U. Michigan)
Explanation: Why would x-ray rings appear around a gamma-ray burst? The surprising answer has little to do with the explosion itself but rather with light reflected off areas of dust-laden gas in our own Milky Way Galaxy. GRB 221009A was a tremendous explosion — a very bright gamma-ray burst (GRB) that occurred far across the universe with radiation just arriving in our Solar System last week. Since GRBs can also emit copious amounts of x-rays, a bright flash of x-rays arrived nearly simultaneously with the gamma-radiation. In this case, the X-rays also bounced off regions high in dust right here in our Milky Way Galaxy, creating the unusual reflections. The greater the angle between reflecting Milky Way dust and the GRB, the greater the radius of the X-ray rings, and, typically, the longer it takes for these light-echoes to arrive.
Tomorrow’s picture: a flowering aurora
伽玛射线爆发周围的X射线环
影像提供: NASA Swift Obs.; 数据提供: B. Cenko (NASA’s GSFC), A. Beardmore (U. Leicester) et al.; 影像处理: J. Miller (U. Michigan)
说明: 为何伽玛射线爆发(GRB)的周围会有X射线环? 答案很意外的和爆发本身无关,而是光受到银河系饱含尘埃的云气反射所致。GRB 221009A是宇宙遥远他处的剧烈爆炸所产生之明亮伽玛射线爆发(GRB),而其辐射直到上星期才传到我们的太阳系这里。因为伽玛射线爆发也会发出大量的X射线,而X射线亮闪几乎与伽玛射线辐射同时抵达。在此范例里,X射线也受到银河系内饱含尘埃的云气之反射,造就了图上的不寻常反射环。而造成反射的银河尘埃云与伽玛射线爆发的视张角愈大,X射线环的半径也随着增大,而一般而言回光抵达的时间延迟就愈长。
明日的图片: a flowering aurora