2019 August 6
The Local Void in the Nearby Universe
Image Credit: R. Brent Tully (U. Hawaii) et al.
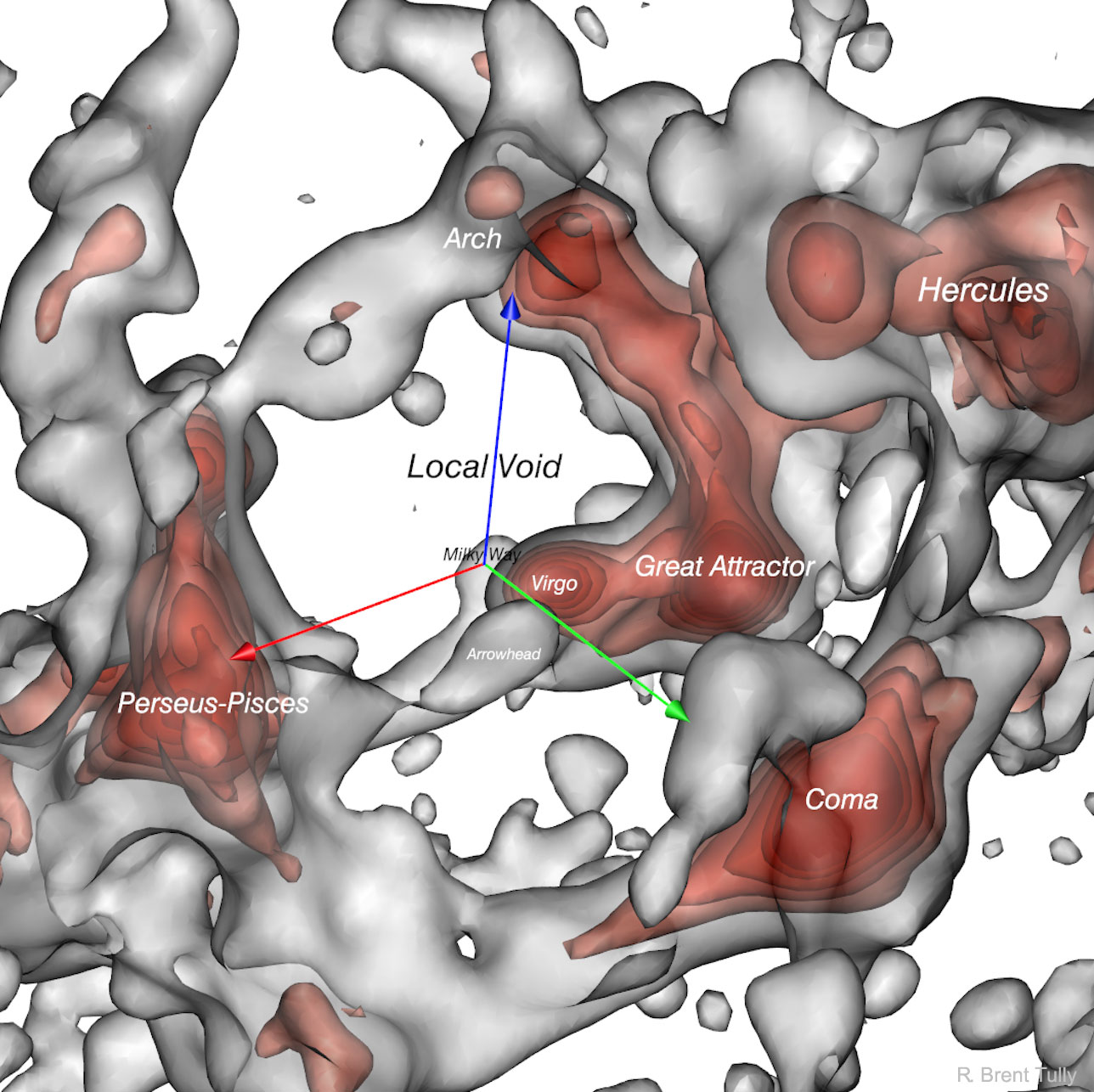
Explanation: What does our region of the Universe look like? Since galaxies are so spread out over the sky, and since our Milky Way Galaxy blocks part of the distant sky, it has been hard to tell. A new map has been made, however, using large-scale galaxy motions to infer what massive objects must be gravitating in the nearby universe. The featured map, spanning over 600 million light years on a side, shows that our Milky Way Galaxy is on the edge of the Virgo Cluster of Galaxies, which is connected to the Great Attractor — an even larger grouping of galaxies. Also nearby are the massive Coma Cluster and the extensive Perseus-Pisces Supercluster. Conversely, we are also on the edge of huge region nearly empty of galaxies known as the Local Void. The repulsive push by the Local Void combined with the gravitational pull toward the elevated galaxy density on the other side of the sky explains part of the mysteriously high speed our Galaxy has relative to the cosmic microwave background — but not all. To explore the local universe yourself, as determined by Cosmicflows-3, you are invited to zoom in and spin around this interactive 3D visualization.
邻近宇宙中的局部空洞
影像来源: R. Brent Tully (U. Hawaii) et al.
说明:我们在宇宙中所处的区域是什么样子的?因为星系散布在广阔的天空中,而且我们的银河系遮挡了部分遥远的天空,所以很难辨别清楚。然而,我们利用大规模的星系运动能推断出在邻近宇宙中肯定有哪些大质量天体受到吸引,从而构建出一幅全新的分布图。这幅一边跨度超过6亿光年的特征分布图呈现出我们的银河系位于室女座星系团的边缘,它与另一个更庞大的星系群-巨引源相连接。附近还有巨大的后发星系团和广袤的英仙-双鱼座超星系团。相反,我们也处在几乎没有星系、名为本巨洞的巨大区域边缘。局部空洞的排斥力加上另一边星系高密度的引力可以部分但不能完全解释为什么我们星系相对于宇宙微波背景,具有这么神秘的高速度。想要亲自探索由Cosmicflows-3判定的本地宇宙,请放大并旋转这幅交互式三维可视化影像。