2020 January 31
Goldilocks Zones and Stars
Infographic Credit: NASA ESA, Z. Levy (STScI)
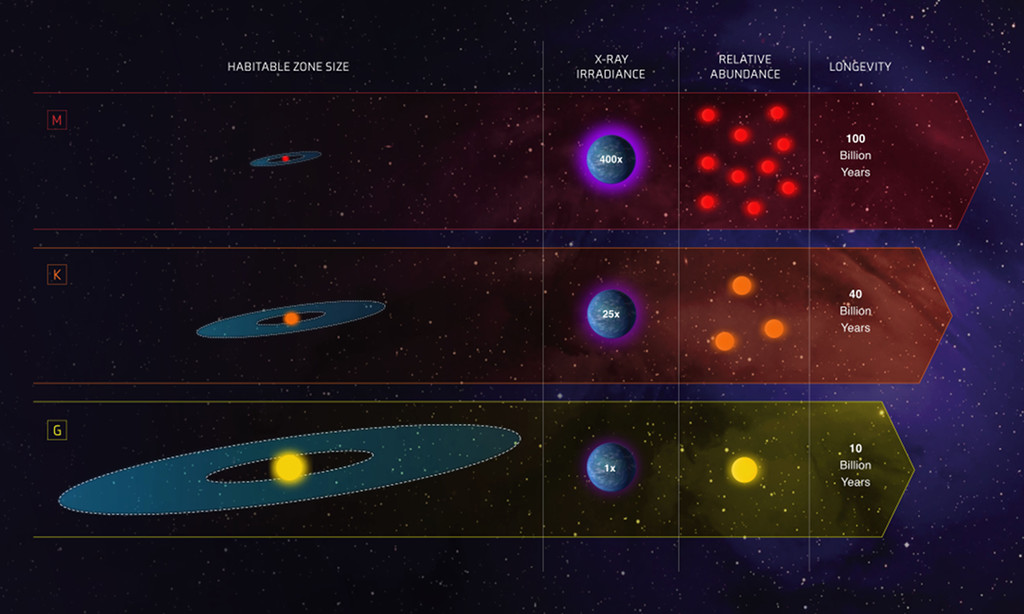
Explanation: The Goldilocks zone is the habitable zone around a star where it’s not too hot and not too cold for liquid water to exist on the surface of orbiting planets. This intriguing infographic includes relative sizes of those zones for yellow G stars like the Sun, along with orange K dwarf stars and red M dwarf stars, both cooler and fainter than the Sun. M stars (top) have small, close-in Goldilocks zones. They are also seen to live long (100 billion years or so) and are very abundant, making up about 73 percent of the stars in the Milky Way. Still, they have very active magnetic fields and may produce too much radiation harmful to life, with an estimated X-ray irradiance 400 times the quiet Sun. Sun-like G stars (bottom) have large Goldilocks zones and are relatively calm, with low amounts of harmful radiation. But they only account for 6 percent of Milky Way stars and are much shorter lived. In the search for habitable planets, K dwarf stars could be just right, though. Not too rare they have 40 billion year lifetimes, much longer than the Sun. With a relatively wide habitable zone they produce only modest amounts of harmful radiation. These Goldilocks stars account for about 13 percent of the stars of the Milky Way.
恒星的宜居带
图解资讯提供: NASA ESA , Z. Levy ( STScI )
说明: 宜居带是指在恒星周围的特定带状区,在其内绕行母星的行星之表面温度冷热适中,让水能以液体的状态存在于表面。这张很有趣的图解资讯,呈现了泛黄G型星(诸如太阳)、橙色K型矮星及泛红M型矮星的宜居带之相对大小,而K型及M型恒星的温度和亮度都比太阳低。很明显的,位在图顶的M型星之宜居带最小,最靠近母星。它们同时也最长寿(寿命长达1,000亿年左右),数量非常多,约占银河星数的73%。不过,它们有非常活跃的磁场,因此会发出太量危害生命的辐射,据估计它们的X射线辐照度,大约是宁静期太阳的400倍。类太阳G型星(最底的图板)有相当大的宜居带,相对宁静,危害辐射的量最少。只不过,它们只占银河星数的6%,而且相对短命。在寻找宜居行星的工作上,K型矮星反而是最佳的目标。因为它们的数量不少,而且400亿年的寿命也远比太阳长。除此之外,它们的宜居带够大,发出的危害辐射也不会过量。这类宜居恒星的数量,占了13%的银河星数。(图标对照:habitable zone size宜居带大小; X-ray irradiance X射线辐照度; relative abudant相对数量; longevity寿命)