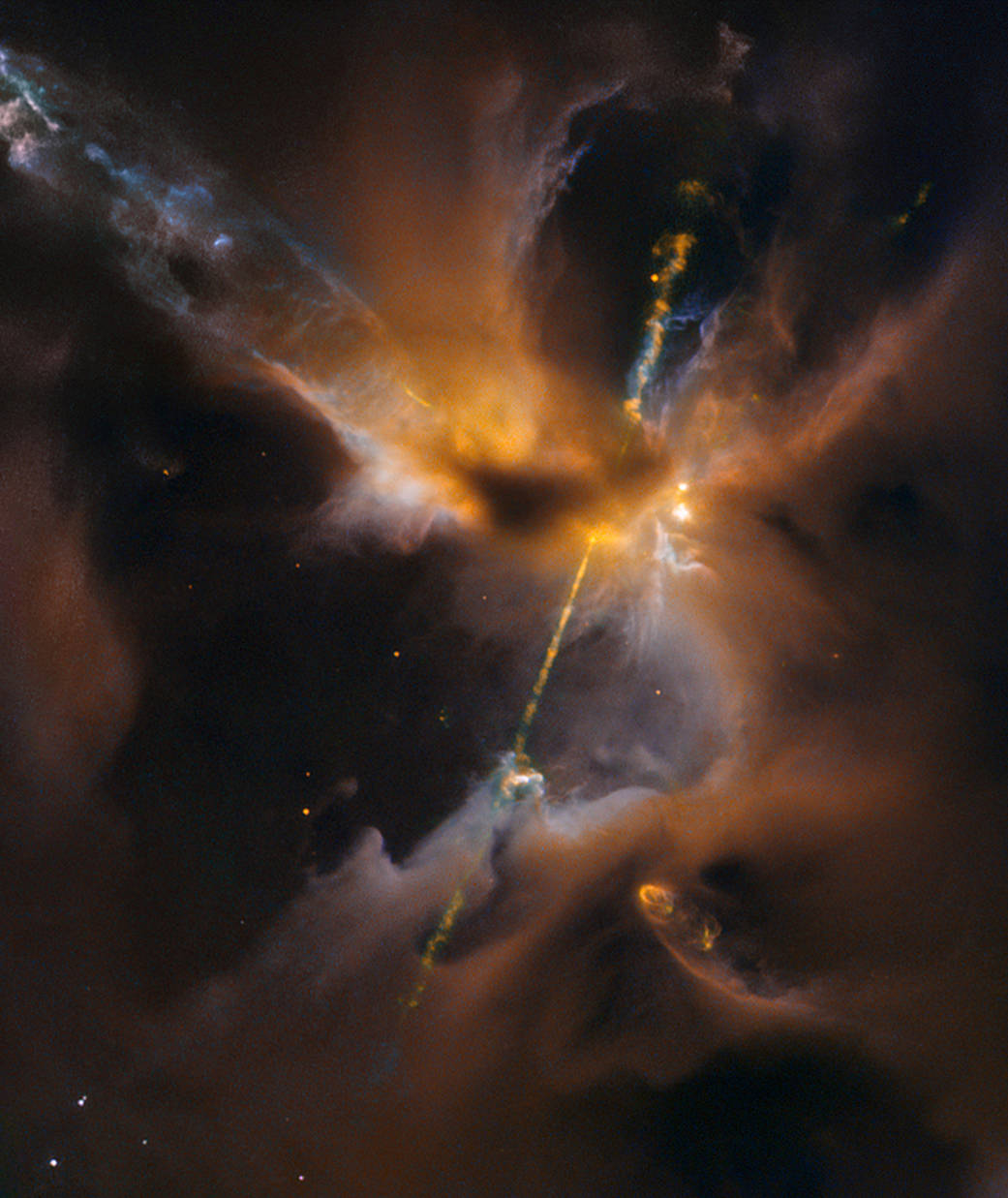
Lying inside our home galaxy, the Milky Way, this Herbig–Haro object is a turbulent birthing ground for new stars in a region known as the Orion B molecular cloud complex, located 1,350 light-years away.
Herbig–Haro (HH) objects are bright patches of nebulosity associated with newborn stars that form when narrow jets of partially ionized gas ejected by stars collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust. This image of Herbig-Haro Jet HH 24 was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2015.
When stars form within giant clouds of cool molecular hydrogen, some of the surrounding material collapses under gravity to form a rotating, flattened disk encircling the newborn star.
Although planets will later congeal in the disk, at this early stage the protostar is feeding on the disk with a voracious appetite. Gas from the disk rains down onto the protostar and engorges it. Superheated material spills away and is shot outward from the star in opposite directions along an uncluttered escape route – the star’s rotation axis.
Shock fronts develop along the jets and heat the surrounding gas to thousands of degrees Fahrenheit. The jets collide with the surrounding gas and dust and clear vast spaces, like a stream of water plowing into a hill of sand.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)/Hubble-Europe (ESA) Collaboration, D. Padgett (GSFC), T. Megeath (University of Toledo), and B. Reipurth (University of Hawaii)
这个赫比格-哈罗天体位于我们的主星系银河系内,是位于1350光年外的猎户座B分子云复合体区域内新生恒星的湍流诞生地。
赫比格-哈罗星云(HH)是与新生恒星有关的明亮星云斑块,当恒星喷射出的狭窄的部分电离气体喷流与附近的气体云和尘埃云相撞时形成。这张Herbig-Haro Jet HH 24的照片由哈勃太空望远镜于2015年拍摄。
当恒星在巨大的冷氢分子云中形成时,周围的一些物质在重力作用下坍缩,形成一个旋转的扁平圆盘,环绕着新生的恒星。
虽然行星稍后会在圆盘中凝结,但在这个早期阶段,原恒星正以贪婪的胃口在圆盘内进食。来自圆盘的气体像雨点一样落在原恒星上并使其膨胀。过热的物质溢出,沿着一条整齐的逃逸路线——恒星的自转轴,从恒星向外朝相反的方向喷射。
激波沿喷流发展,将周围的气体加热到华氏数千度。喷射流与周围的气体和尘埃相撞,并清除了广阔的空间,就像一股水流冲入沙丘。
影像来源: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)/Hubble-Europe (ESA) Collaboration, D. Padgett (GSFC), T. Megeath (University of Toledo), and B. Reipurth (University of Hawaii)