Future lunar landers might come equipped with 3D printed rocket engine parts that help bring down overall manufacturing costs and reduce production time. NASA is investing in advanced manufacturing – one of five industries of the future – to make it possible.
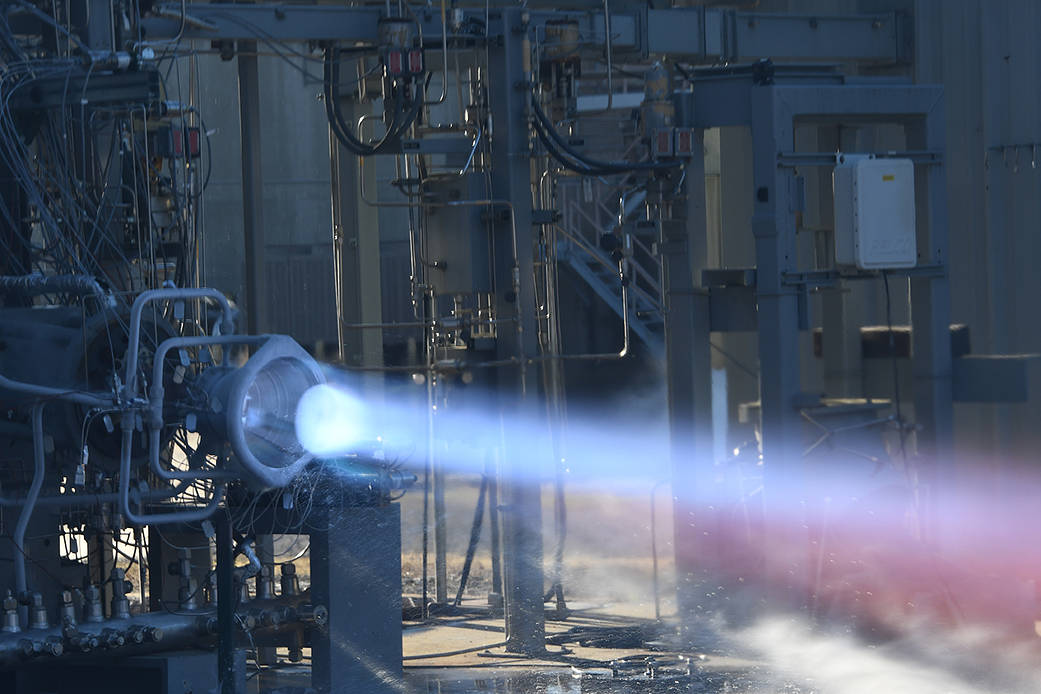
Through a series of hot-fire tests in November, NASA demonstrated that two additively manufactured engine components – a copper alloy combustion chamber and nozzle made of a high-strength hydrogen resistant alloy – could withstand the same extreme combustion environments that traditionally manufactured metal structures experience in flight.
This image shows the hot-fire testing of an additively manufactured copper alloy combustion chamber and a nozzle made of a high-strength hydrogen resistant alloy.
Learn more about the 3D printing process.
Image Credit: NASA
未来的月球着陆器可能会配备3D打印的火箭发动机零件,以帮助降低总体制造成本并减少生产时间。 NASA正在投资于先进制造业(未来的五个行业之一)以使其成为可能。
通过11月的一系列热燃测试,NASA证明了两种额外制造的发动机部件——一个铜合金燃烧室和由高强度抗氢合金制成的喷嘴——可以与传统制造的金属结构在飞行中经受同样的极端燃烧环境。
这张照片显示了一个额外制造的铜合金燃烧室和一个高强度抗氢合金喷嘴的热测试。
图片来源:NASA







coolllllll