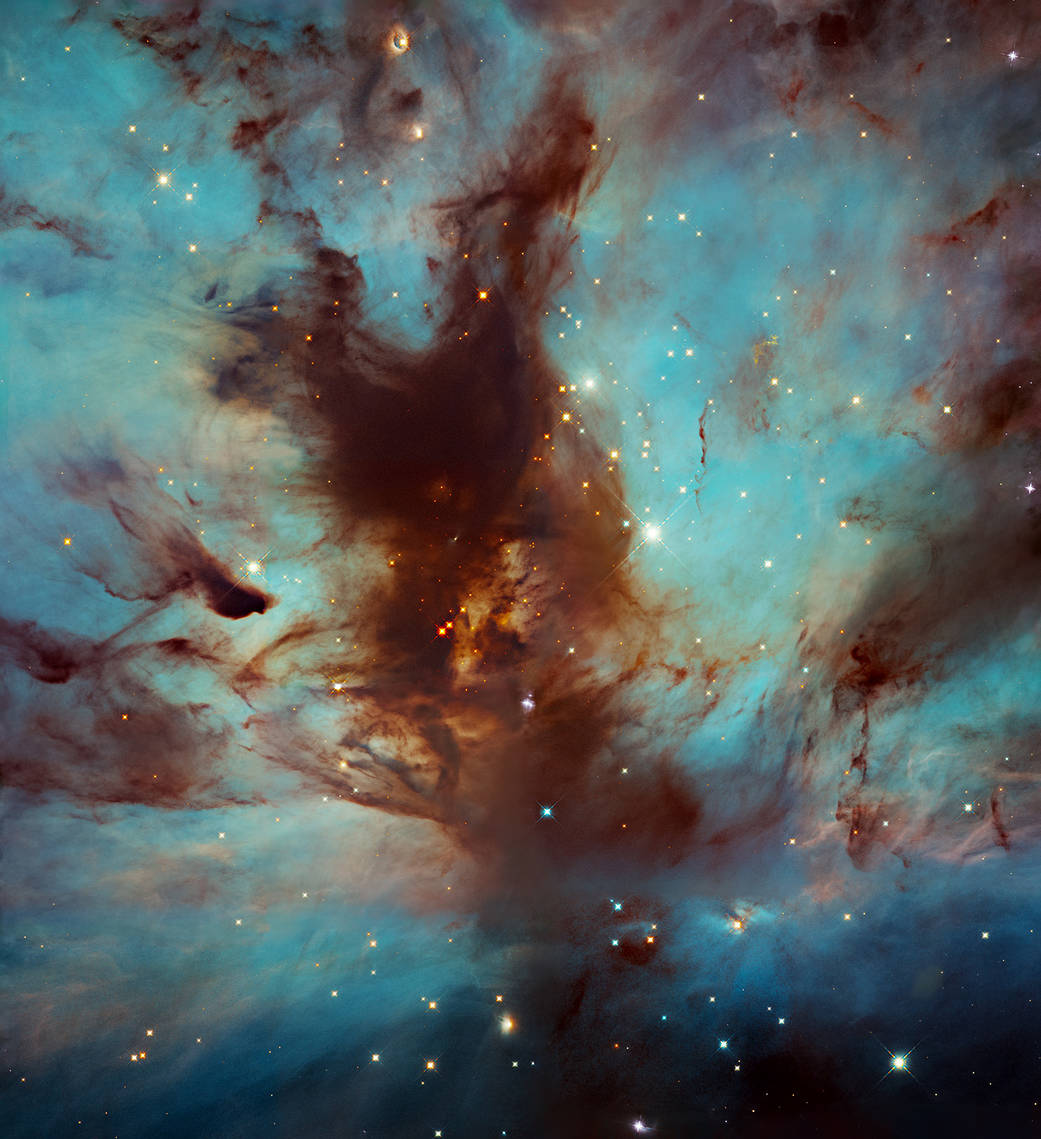
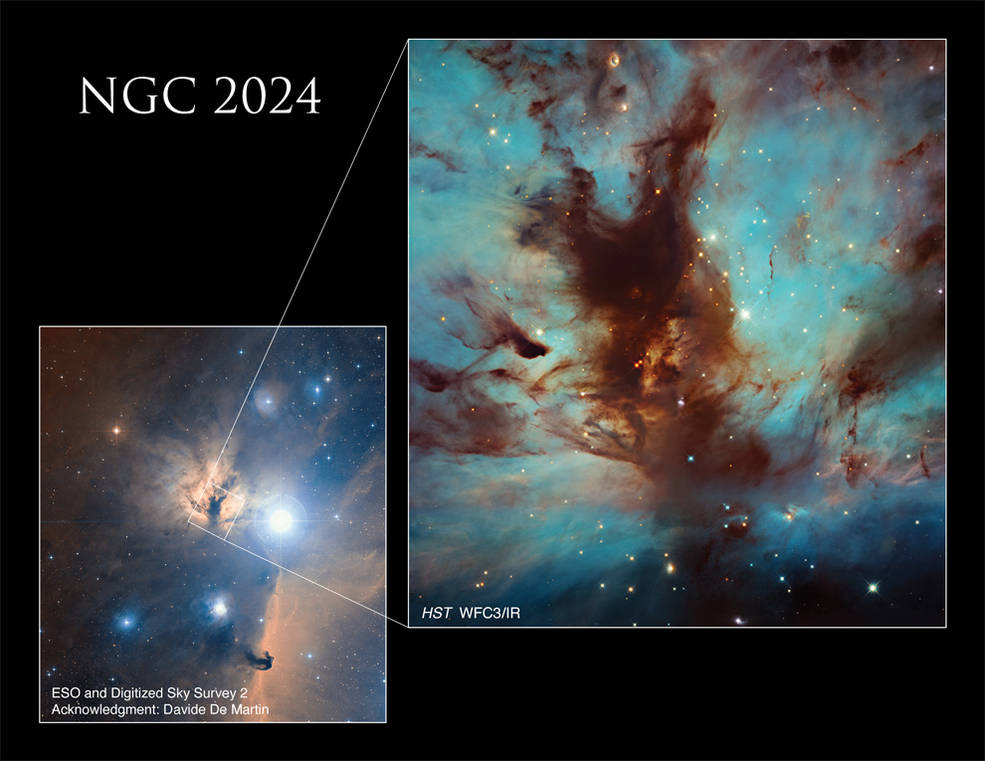
The Flame Nebula, also called NGC 2024, is a large star-forming region in the constellation Orion that lies about 1,400 light-years from Earth. It’s a portion of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which includes such famous nebulae as the Horsehead Nebula and Orion Nebula. This image focuses on the dark, dusty heart of the nebula, where a star cluster resides, mostly hidden from view. Nearby (but not visible in this image) is the bright star Alnitak, the easternmost star in the Belt of Orion. Radiation from Alnitak ionizes the Flame Nebula’s hydrogen gas. As the gas begins to cool from its higher-energy state to a lower-energy state, it emits energy in the form of light, causing the visible glow behind the swirled wisps of dust.
火焰星云,也称为NGC2024,是猎户座的一个大型恒星形成区域,距离地球约1400光年。它是猎户座分子云复合体的一部分,其中包括马头星云和猎户座星云等著名星云。这张图片聚焦于星云黑暗、充满尘埃的中心地带,那里有一个星团,大部分都隐藏在视线之外。附近(但在这张照片中看不到)是明亮的恒星参宿一,猎户座带最东端的恒星。来自参宿一的辐射使火焰星云的氢气电离。当气体开始从高能状态冷却到低能状态时,它会以光的形式释放能量,在旋转的尘埃后面产生可见的辉光。
Researchers have used Hubble to measure the mass of stars in the cluster as they search for brown dwarfs, a type of dim object that’s too hot and massive to be classified as a planet but also too small and cool to shine like a star.
研究人员在寻找棕矮星的过程中,利用哈勃望远镜测量了星团中恒星的质量。这是一种昏暗的天体,其温度和质量太高,不能被归类为行星,但与恒星比较却太小和太冷,不能像恒星一样发光。
The Flame Nebula, also called NGC 2024, is part of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex and is found near the Horsehead Nebula.
Credits: NASA, ESA, and N. Da Rio (University of Virginia), ESO, DSS2, and D. De Martin; Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)
火焰星云,也称为NGC2024,是猎户座分子云复合体的一部分,位于马头星云附近。
影像来源: NASA, ESA, and N. Da Rio (University of Virginia), ESO, DSS2, and D. De Martin; 影像处理: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)
Main Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and N. Da Rio (University of Virginia); Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)
主图来源: NASA, ESA, and N. Da Rio (University of Virginia); Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)