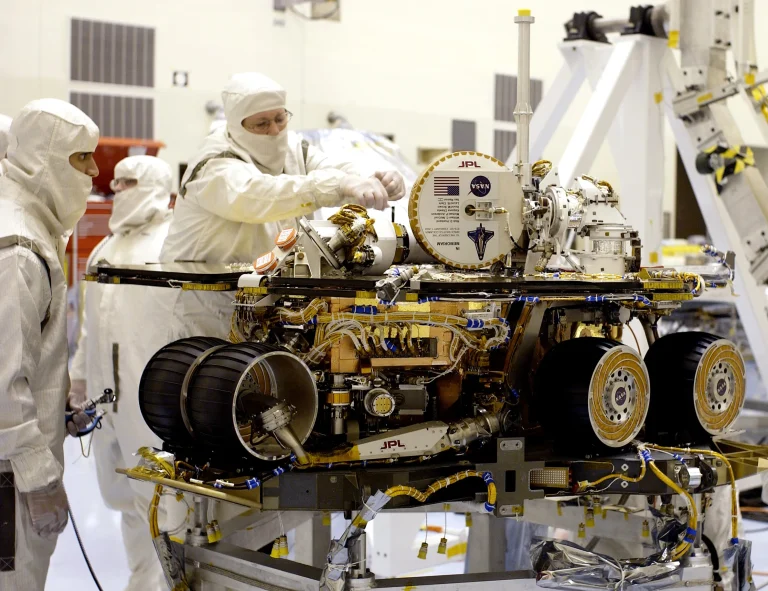
美国强大的新型深空火箭,美国宇航局的太空发射系统,在发射美国宇航局的猎户座飞船和潜在的货物到月球轨道时,将面临恶劣的条件和极端的温度,为此,它需要强有力的保护。
技术人员和工程师已经通过了3D打印技术,可以将热保护系统应用到火箭更小、更复杂的部件上。喷涂泡沫或传统绝缘材料适用于SLS的大型和小型部件;它可以在发射过程中保护火箭免受热量的影响,并使大型燃料箱中的推进剂保持低温。然而,小型硬件或狭窄区域(如发动机部分的内部管道)需要技术人员手动喷涂泡沫或在某些情况下使用3D打印模具进行泡沫铸造。在此过程中,混合并倒入模具中的泡沫膨胀,以完美贴合零件。这减少了复杂和繁琐的后处理修剪的需要,从而减少了总体处理时间。美国宇航局和波音公司的工程师在项目早期就进行了广泛的开发和鉴定。使用这些数据,该团队开发了一种精细的工艺,减少了认证单个3D打印模具所需的时间,并使团队能够将更多时间用于满足每个飞行泡沫应用必须满足的关键要求。这简化了从3D打印到浇筑应用程序的过程,并允许更快的处理时间。
美国宇航局负责在2024年前将美国宇航员送上月球。我们深空探索的支柱是SLS和猎户座,它将从美国宇航局位于佛罗里达州的肯尼迪航天中心发射到月球轨道的门户(Gateway)。从那里,宇航员最终将使用一种拟建的人类登月系统执行登月任务。
America’s powerful new deep space rocket, NASA’s Space Launch System, will face harsh conditions and extreme temperatures in flight when launching NASA’s Orion spacecraft and potential cargo to lunar orbit, and for that, it’ll need strong protection.
Technicians and engineers have qualified 3D printing to aid in the application of the thermal protection system to the smaller, more intricate parts of the rocket. Spray-on foam or traditional insulation is applied to both large and small components of SLS; it protects the rocket from heat during launch and keeps the propellant within the large tanks cold. However, small hardware or cramped areas like the internal ducts of the engine section require technicians to either manually spray the foam on or apply a foam casting using, in some cases, a 3D printed mold. During the process, the foam, which is mixed and poured into the mold, expands to perfectly fit the part. This decreases overall processing time by reducing the need for complex and tedious post-process trimming. NASA and Boeing engineers performed extensive development and qualification pour foam testing early in the program. Using this data, the team developed a refined process that reduced the amount of time required to certify individual 3D printed molds and allowed the team to spend more time focusing on the critical requirements that must be met for each flight foam application. This streamlined the process, from 3D printing to pour application, and allowed for quicker processing times.
NASA is charged to get American astronauts to the Moon by 2024. Our backbone for deep space exploration is SLS and Orion, which will launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Gateway in lunar orbit. From there, astronauts will ultimately use a proposed human lunar landing system for missions to the surface of the Moon.
Image Credit: Boeing