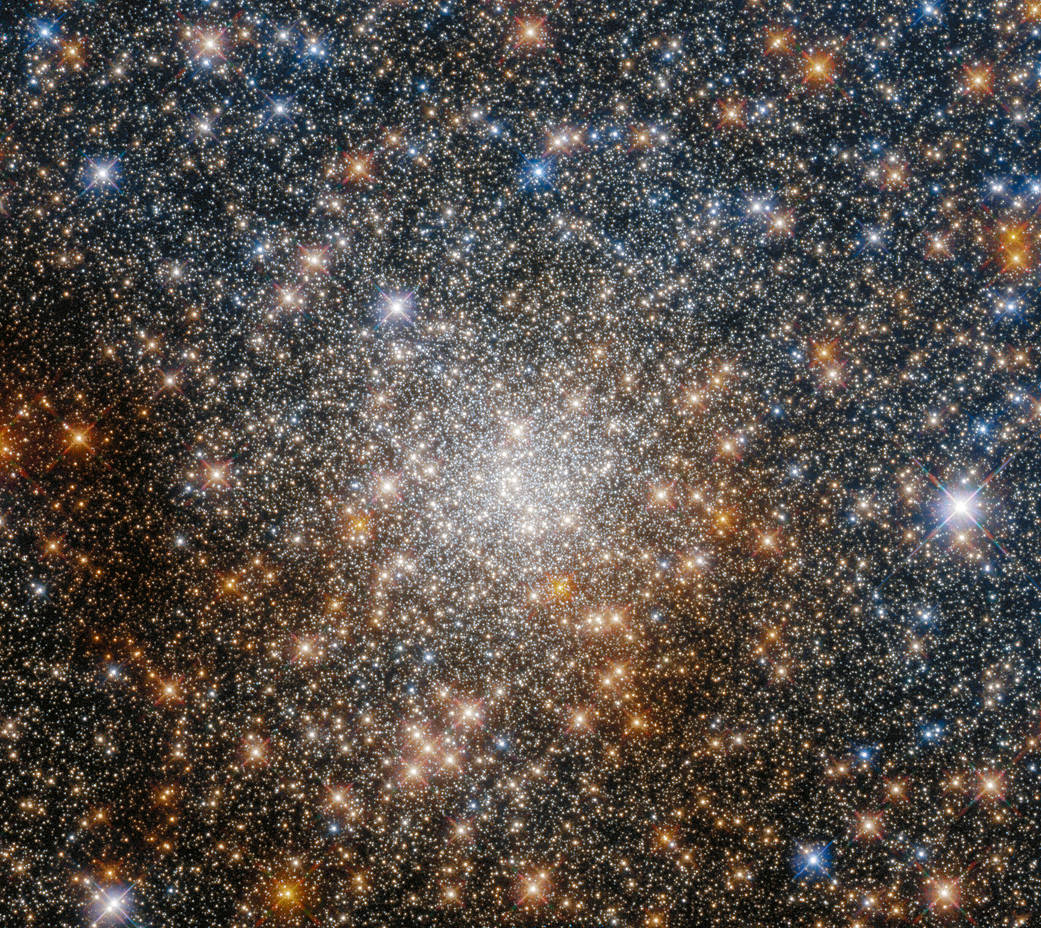
The Hubble Space Telescope captured this glittering scene using its Wide Field Camera 3 and Advanced Camera for Surveys.
Globular clusters are stable, tightly bound groups of tens of thousands to millions of stars. As this image demonstrates, the hearts of globular clusters are densely packed with stars. Terzan 9 is dotted with so many glittering stars that it resembles a sea of sequins.
This starry snapshot is from a Hubble program investigating globular clusters located toward the heart of the Milky Way, in which its central region holds a tightly packed group of stars known as the galactic bulge, an area rich in interstellar dust. This dust makes globular clusters near the galaxy’s center difficult to study, as it absorbs starlight and can even change the apparent colors of stars in these clusters. Hubble’s sensitivity at both visible and infrared wavelengths allows astronomers to measure how star colors change due to interstellar dust. Knowing a star’s true color and brightness allows astronomers to estimate its age, and thereby estimate the globular cluster’s age.
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen
哈勃太空望远镜用它的广角相机3号和高级巡天相机捕捉到了这一闪闪发光的景象。
球状星团是由数万到数百万颗恒星组成的稳定、紧密结合的星团。正如这张图片所示,球状星团的中心密布着恒星。Terzan 9星光熠熠,犹如一片亮片之海。
这张星空快照来自一个哈勃项目,该项目调查了位于银河系中心的球状星团,其中它的中心区域拥有一组紧密排列的恒星,称为银河系凸起,这是一个富含星际尘埃的区域。这种尘埃使星系中心附近的球状星团难以研究,因为它会吸收星光,甚至可以改变这些星团中恒星的表观颜色。哈勃对可见光和红外波长的敏感度使天文学家能够测量恒星颜色如何因星际尘埃而变化。了解恒星的真实颜色和亮度可以让天文学家估计它的年龄,从而估计球状星团的年龄。
影像来源:ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen