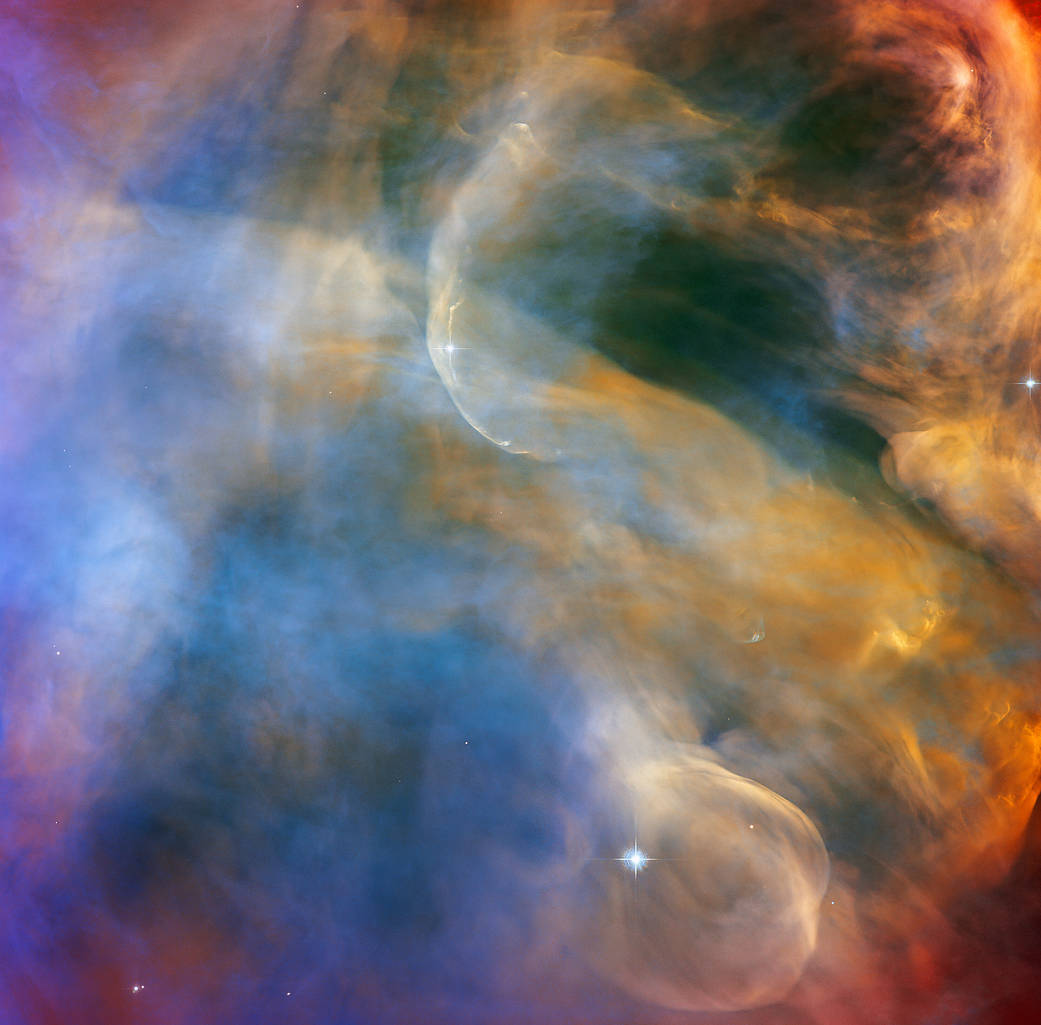
This celestial cloudscape from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope captures the colorful region in the Orion Nebula surrounding the Herbig-Haro object HH 505. Herbig-Haro objects are luminous regions surrounding newborn stars that form when stellar winds or jets of gas spew from these infant stars creating shockwaves that collide with nearby gas and dust at high speeds. In the case of HH 505, these outflows originate from the star IX Ori, which lies on the outskirts of the Orion Nebula around 1,000 light-years from Earth. The outflows themselves are visible as gracefully curving structures at the top and bottom of this image. Their interaction with the large-scale flow of gas and dust from the core of the nebula distorts them into sinuous curves.
Captured with Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) by astronomers studying the properties of outflows and protoplanetary disks, the image reveals bright shockwaves formed by the outflows as well as slower moving currents of stellar material. The Orion Nebula is awash in intense ultraviolet radiation from bright young stars. Hubble’s sensitivity to ultraviolet light allows astronomers to directly observe these high-energy outflows and learn more about their structures.
The Orion Nebula is a dynamic region of dust and gas where thousands of stars are forming. It is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth, making it one of the most scrutinized areas of the night sky and often a target for Hubble. This observation was also part of a spellbinding Hubble mosaic of the Orion Nebula, which combined 520 ACS images in five different colors to create the sharpest view ever taken of the region.
Text credit: European Space Agency (ESA)
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Bally; Acknowledgment: M. H. Özsaraç
这幅来自NASA/ESA哈勃太空望远镜的天体云图捕捉到了围绕猎户座星云中赫比格-哈罗天体HH 505的彩色区域。赫比格-哈罗天体是围绕在新生恒星周围的发光区域,当这些新生恒星喷出恒星风或气体喷流时,会产生冲击波,与附近的气体和尘埃高速碰撞。以HH 505为例,这些喷流出来自猎户座IX星,它位于猎户座星云的外围,距离地球约1,000光年。在这张图像的顶部和底部,可以看到喷流本身是优雅的曲线结构。它们与来自星云核心的大规模气体和尘埃流的相互作用使它们扭曲成弯曲的曲线。
研究外流和原行星盘特性的天文学家用哈勃高级巡天相机(ACS)研究了喷流和原行星盘的特性,这张照片揭示了喷流形成的明亮冲击波,以及缓慢移动的恒星物质流。猎户座星云沐浴在明亮的年轻恒星发出的强烈紫外线辐射中。哈勃望远镜对紫外线的敏感度让天文学家可以直接观察到这些高能喷流,并更多地了解它们的结构。
猎户座星云是一个充满尘埃和气体的动态区域,数千颗恒星正在这里形成。它是离地球最近的大质量恒星形成区域,是夜空中最受关注的区域之一,经常是哈勃望远镜的目标。这一观测也是哈勃猎户座星云拼图的一部分,该拼图将520张五种不同颜色的ACS图像组合在一起,形成了该区域有史以来最清晰的图像。
文字来源:欧洲航天局 (ESA)
图片来源:ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Bally;致谢:M.H. Özsaraç