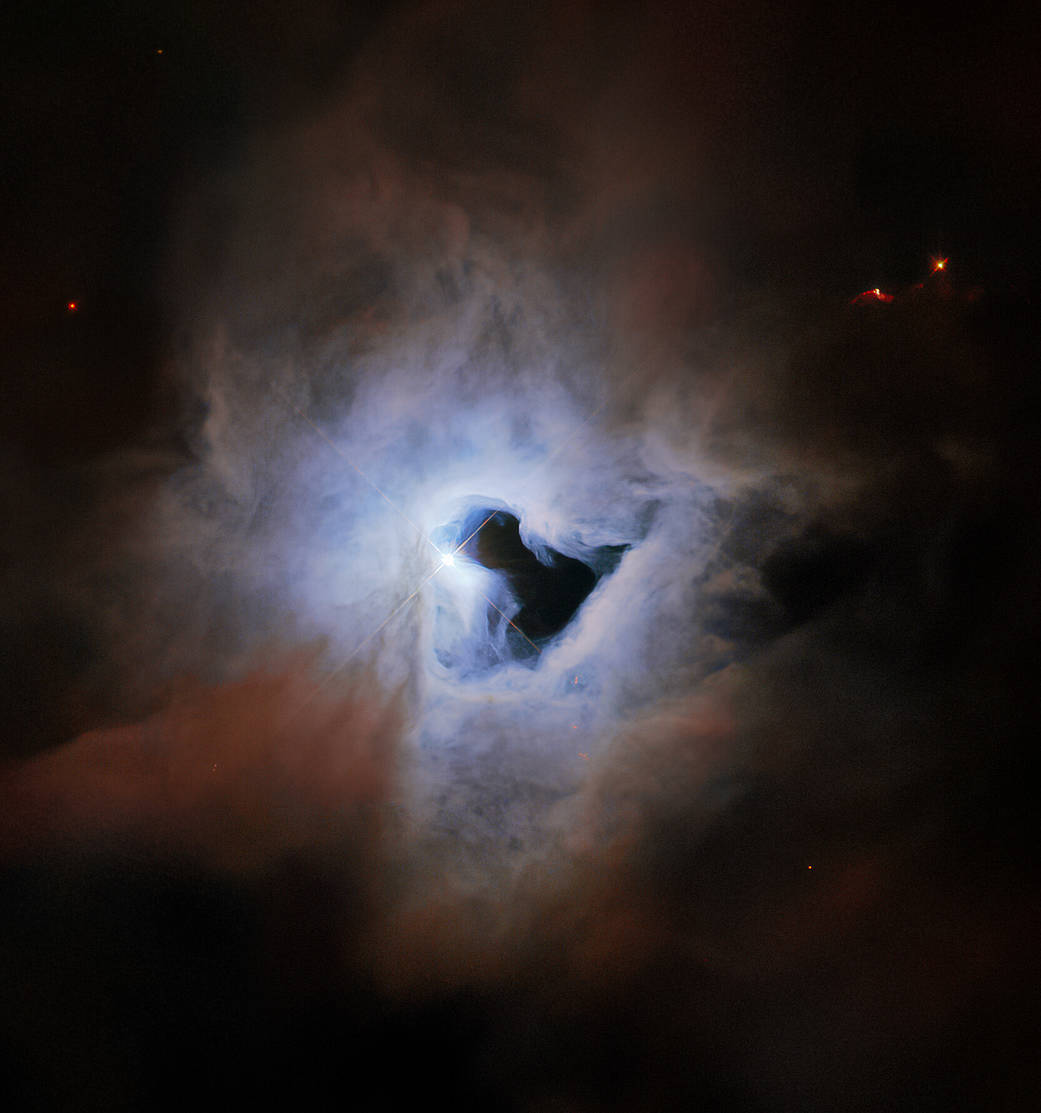
This peculiar portrait from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope showcases NGC 1999, a reflection nebula in the constellation Orion. NGC 1999 is around 1,350 light-years from Earth and lies near the Orion Nebula, the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. NGC 1999 itself is a relic of recent star formation – it is composed of debris left over from the formation of a newborn star.
Just like fog curling around a streetlamp, reflection nebulae like NGC 1999 shine by the light from an embedded source. In the case of NGC 1999, this source is the aforementioned newborn star V380 Orionis, which is visible at the center of this image. The most notable aspect of NGC 1999’s appearance, however, is the conspicuous hole in its center, which resembles an inky black keyhole of cosmic proportions.
This image was created from archival Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 observations that date from shortly after Servicing Mission 3A in 1999. At the time, astronomers believed that the dark patch in NGC 1999 was something called a Bok globule – a dense, cold cloud of gas, molecules, and cosmic dust that blots out background light. However, follow-up observations using a collection of telescopes, including ESA’s Herschel Space Observatory, revealed that the dark patch is actually an empty region of space. The origin of this unexplained rift in the heart of NGC 1999 remains unknown.
Text credit: European Space Agency (ESA)
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, ESO, K. Noll
这幅来自NASA/ESA哈勃太空望远镜的奇特照片展示了猎户座反射星云NGC 1999。NGC 1999距离地球大约1350光年,位于猎户座星云附近,猎户座星云是离地球最近的大质量恒星形成区域。NGC 1999本身是近期恒星形成的遗迹——它由新生恒星形成时留下的碎片组成。
就像笼罩在街灯周围的雾一样,像NGC 1999这样的反射星云被嵌入的光源发出的光照亮。在NGC 1999的例子中,这个光源就是前面提到的新生恒星猎户座V380,它在这张照片的中央可见。然而,NGC 1999的外观最引人注目的地方是它中心的一个明显的洞,它就像一个宇宙比例的墨黑钥匙孔。
这幅图像是由存档的广域行星相机2号的观测数据生成的,这些数据可以追溯到1999年执行3A任务后不久。当时,天文学家认为NGC 1999中的暗斑是一种叫做博克球状体的东西——一种由气体、分子和宇宙尘埃组成的致密冷云,遮蔽了背景光。然而,使用包括欧空局的赫歇尔太空天文台在内的一系列望远镜进行的后续观测表明,这片黑暗区域实际上是一个空的太空区域。NGC 1999中心这条无法解释的裂缝的起源仍然未知。
文字来源:European Space Agency (ESA)
影像来源:ESA/Hubble & NASA, ESO, K. Noll