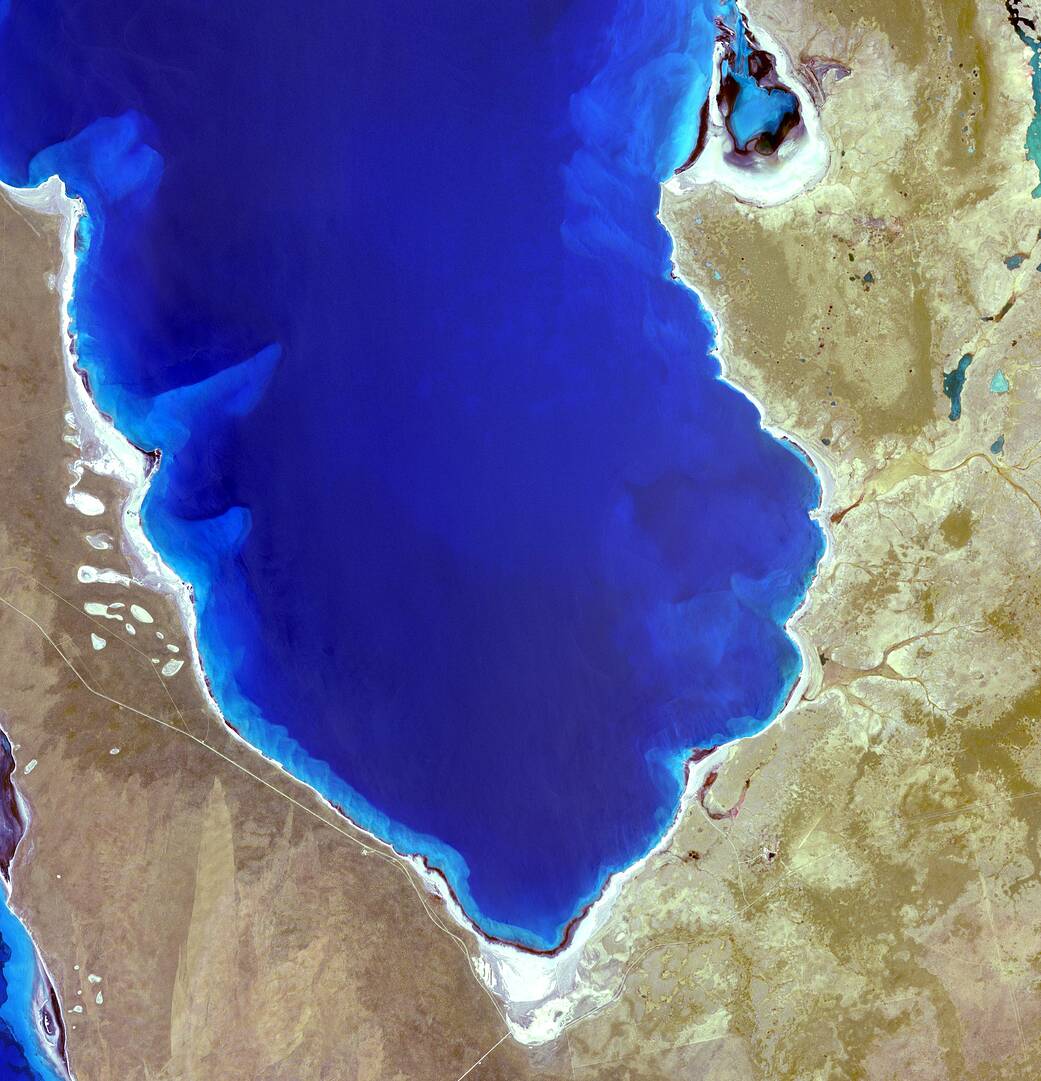
Hamelin Pool Marine Nature Reserve, seen here in an image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on the Terra spacecraft on Dec. 30, 2010, is a special site. Located in the Shark Bay World Heritage Site in Western Australia, it is one of the very few places in the world where we can find living stromatolites—the first living examples of structures built by cyanobacteria. Photosynthetic cyanobacteria are thought to have changed the course of life’s evolution on Earth by playing an important role in the oxygenation of Earth’s atmosphere roughly 2.3 billion years ago. Also, NASA and other federal agencies monitor levels of cyanobacteria, as toxic levels of the blue-green algae can have negative effects on health.
ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. The instrument was built by Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team handles validation and calibration of the instrument and data products.
Image Credit: NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team
哈梅林池海洋自然保护区是一个特殊的地点,这是2010年12月30日由Terra航天器上的先进星载热辐射与反射辐射计(ASTER)拍摄的图像。它位于澳大利亚西部的鲨鱼湾世界遗产遗址,是世界上为数不多的可以发现活的叠层石的地方之一——这是第一个由蓝藻建造的结构的活例子。大约23亿年前,光合作用的蓝藻在地球大气的氧化作用中发挥了重要作用,被认为改变了地球上生命的进化过程。此外,NASA和其他联邦机构也在监测蓝藻的水平,因为蓝藻的毒性水平会对健康产生负面影响。
ASTER是1999年12月18日发射到地球上的五个地球观测仪器之一。ASTER拥有从可见光到热红外波段的14个光谱波段,其高空间分辨率为15至90米(约50至300英尺),可以对地球进行成像,以绘制和监测地球表面的变化。该仪器由日本经济产业省制造。美国/日本联合科学团队负责仪器和数据产品的验证和校准。
影像来源:NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team