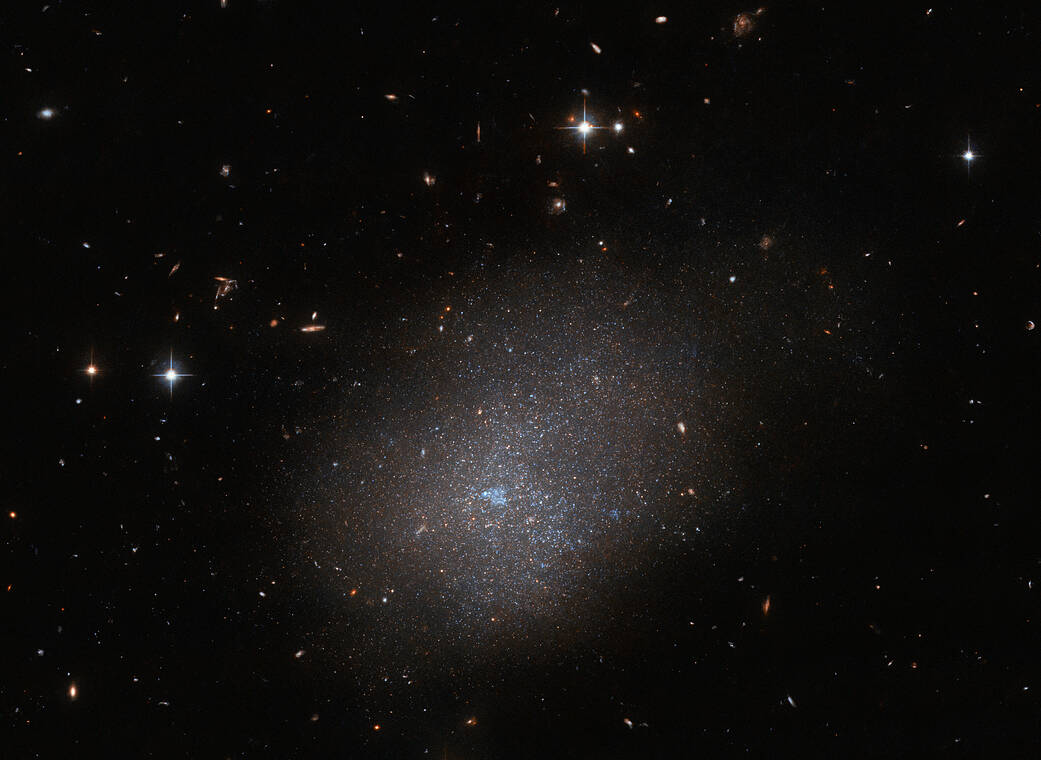
The galaxy ESO 300-16 looms over this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. This galaxy, which lies 28.7 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Eridanus, is a ghostly assemblage of stars which resembles a sparkling cloud. Other distant galaxies and foreground stars complete this astronomical portrait, which was captured by the Advanced Camera for Surveys.
This observation is one of a series which aims to get to know our galactic neighbors. Hubble has observed around three quarters of known galaxies within about 10 megaparsecs of Earth in enough detail to resolve their brightest stars and establish distances to these galaxies. A team of astronomers proposed using small gaps in Hubble’s observing schedule to acquaint ourselves with the remaining quarter of these nearby galaxies.
The megaparsec – meaning one million parsecs – is a unit used by astronomers to chart the mind-bogglingly large distances involved in astronomy. The motion of Earth around the Sun means that stars appear to slightly shift against very distant stars over the course of a year. This small shift is referred to as parallax and is measured in angular units: degrees, minutes, and seconds. One parsec is equivalent to the distance creating a parallax of one-arcsecond and is equivalent to 3.26 light-years or 30.9 trillion kilometers (19.2 trillion miles). The closest star to the Sun is Proxima Centauri, which lies 1.3 parsecs away.
Text credit: European Space Agency (ESA)
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Tully
这张由NASA/ESA哈勃太空望远镜拍摄的照片上,星系ESO 300-16若隐若现。这个星系位于波江座,距离地球2870万光年,是一个幽灵般的群星组合,看起来就像一团闪闪发光的云。其他遥远的星系和前景恒星完成了这幅天文肖像,这是由高级巡天相机拍摄的。
这次观测是一系列旨在了解我们银河系邻居的观测之一。哈勃望远镜已经观测了大约四分之三的已知星系,这些星系距离地球大约10兆秒差距,足够详细地分辨出它们最亮的恒星,并确定了到这些星系的距离。一组天文学家团队提议利用哈勃望远镜观测计划中的少量间隙来了解剩下四分之一的邻近星系。
兆秒差距是天文学家用来表示天文学中涉及的无法想象的巨大距离的单位。地球绕太阳运动意味着星星看起来在一年的时间里相对于非常遥远的星星会有微小的移动。这种微小的位移被称为视差,以角度单位来度量:度、分和秒。一秒差距相当于视差为1角秒的距离,相当于3.26光年或30.9万亿公里(19.2万亿英里)。离太阳最近的恒星是比邻星,距离太阳1.3秒差距。
文字来源: 欧洲航天局 (ESA)
图片来源: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Tully