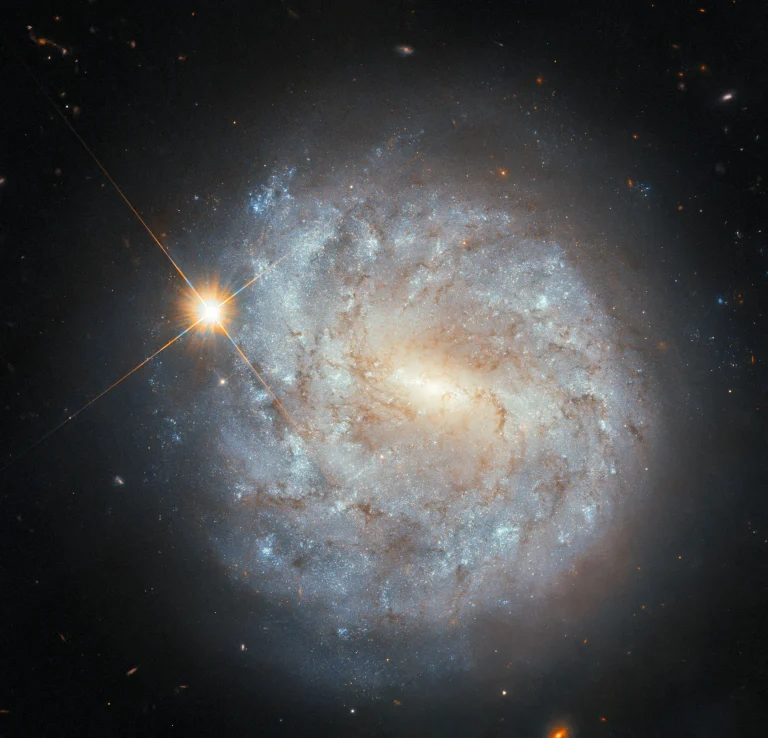
这个发光的天体是星系NGC 4621,更广为人知的名字是Messier 59。正如后一个名字所示,这个星系被列在18世纪法国彗星猎人查尔斯·梅西耶编撰的著名的深空天体目录中。然而,德国天文学家约翰·戈特弗里德·克勒(Johann Gottfried Koehler)在梅西耶(Messier)于1779年将这颗星系加入他的收藏前几天发现了这颗星系。
现代观测表明,Messier 59是一个椭圆星系,是与螺旋星系和不规则星系并列的三大类星系之一。椭圆星系往往是这三个星系中进化得最快的,充满了古老的红色恒星,几乎没有或几乎没有新恒星的形成。然而,Messier 59在某种程度上与这一趋势背道而驰;该星系确实显示出恒星形成的迹象,一些新生恒星位于靠近核心的圆盘内。
Messier 59位于室女座(处女座)内2000多个室女座星系团中,距离我们大约5000万光年。这张照片是由美国宇航局/欧洲航天局哈勃太空望远镜的高级巡天照相机拍摄的。
Messier 59出现在哈勃的Messier目录中,其中包括一些可以从地球北半球观测到的最迷人的天体。在以下网址查看更多NASA处理的图像和其他Messier天体:https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/hubble-s-messier-catalog
文字来源:ESA (欧洲航天局)
图像来源:Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, P. Cote
This luminous orb is the galaxy NGC 4621, better known as Messier 59. As this latter moniker indicates, the galaxy is listed in the famous catalog of deep-sky objects compiled by French comet-hunter Charles Messier in the 18th century. However, German astronomer Johann Gottfried Koehler is credited with discovering the galaxy just days before Messier added it to his collection in 1779.
Modern observations show that Messier 59 is an elliptical galaxy, one of the three main kinds of galaxies along with spirals and irregulars. Ellipticals tend to be the most evolved of the trio, full of old, red stars and exhibiting little or no new star formation. Messier 59, however, bucks this trend somewhat; the galaxy does show signs of star formation, with some newborn stars residing within a disk near the core.
Located in the 2,000-strong Virgo cluster of galaxies within the constellation of Virgo (the Virgin), Messier 59 lies approximately 50 million light-years away from us. This image was taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Advanced Camera for Surveys.
Messier 59 is featured in Hubble’s Messier catalog, which includes some of the most fascinating objects that can be observed from Earth’s Northern Hemisphere. See the NASA-processed image and other Messier objects at: https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/hubble-s-messier-catalog.
Text credit: ESA (European Space Agency)
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, P. Cote