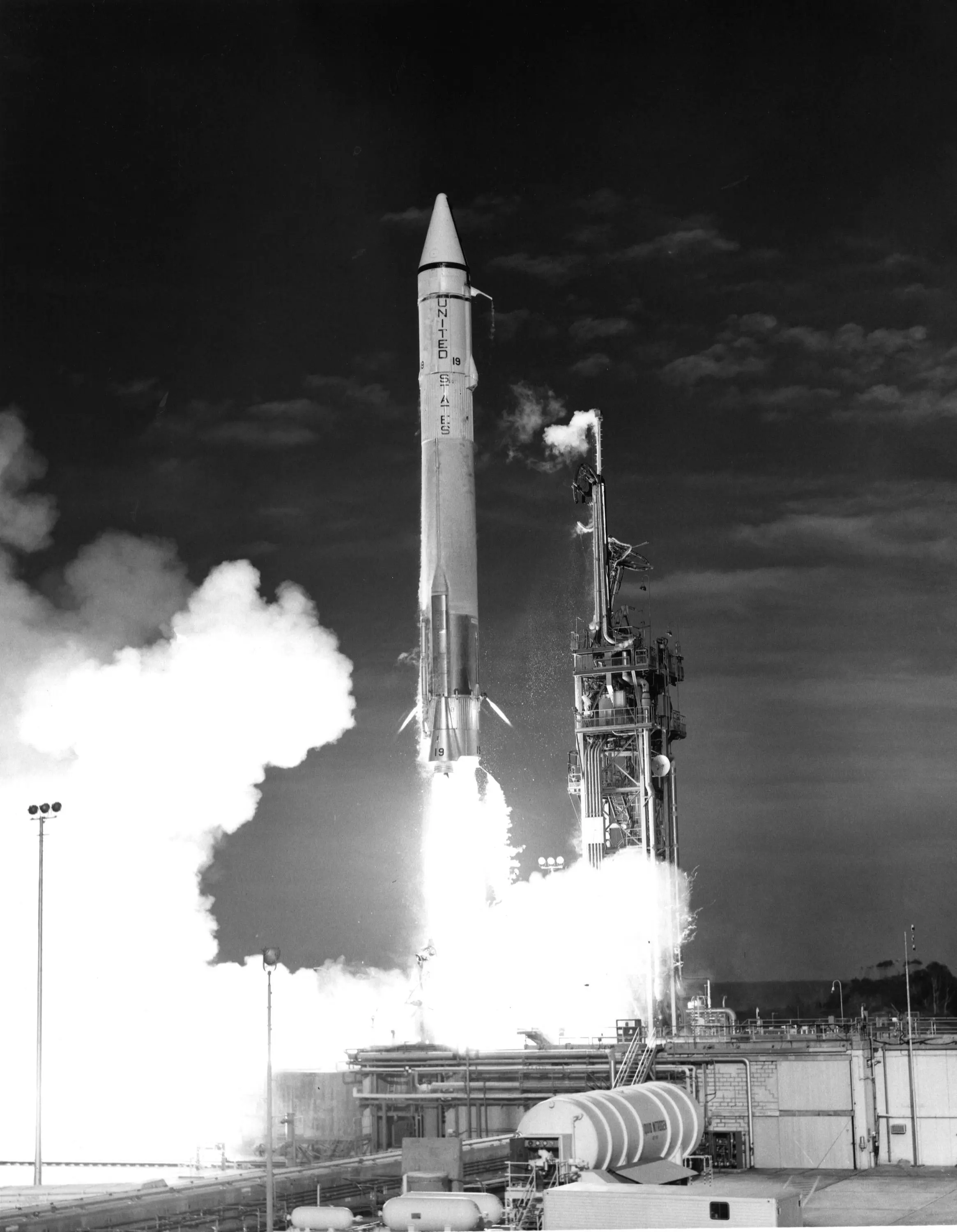
55 years ago, on March 27, 1969, an Atlas-Centaur rocket launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, sending Mariner 7 on its way to study Mars. Mariner 7 was the second Mars probe; Mariner 6 launched Feb. 24, 1969, to investigate Mars’ equator. Mariner 7 made a close flyby of Mars just five days after Mariner 6. Scientists were able to instruct it to take additional pictures of the south pole, which had piqued their interest during Mariner 6’s flyby.
The Mariner program launched 10 missions to explore Mercury, Venus, and Mars through flybys or orbits. These missions proved that interplanetary exploration was workable with small, low-cost spacecraft, laying the groundwork for all the deep space exploration missions that followed.
Image Credit: NASA
55年前的1969年3月27日,一枚阿特拉斯-半人马座火箭从佛罗里达州的NASA肯尼迪航天中心发射升空,将水手7号送上了研究火星的旅程。水手7号是第二个火星探测器;水手6号于1969年2月24日发射,以调查火星的赤道。水手号7号在水手号6号飞掠火星五天后,水手7号近距离飞掠火星。科学家们能够指示它拍摄更多的南极照片,这个区域在水手号6号的飞掠期间引起了他们的兴趣。
水手计划发射了10次任务,通过飞掠或环绕探测水星、金星和火星。这些任务证明,利用小型低成本航天器进行星际探索是可行的,为随后的所有深空探索任务奠定了基础。
影像来源:NASA