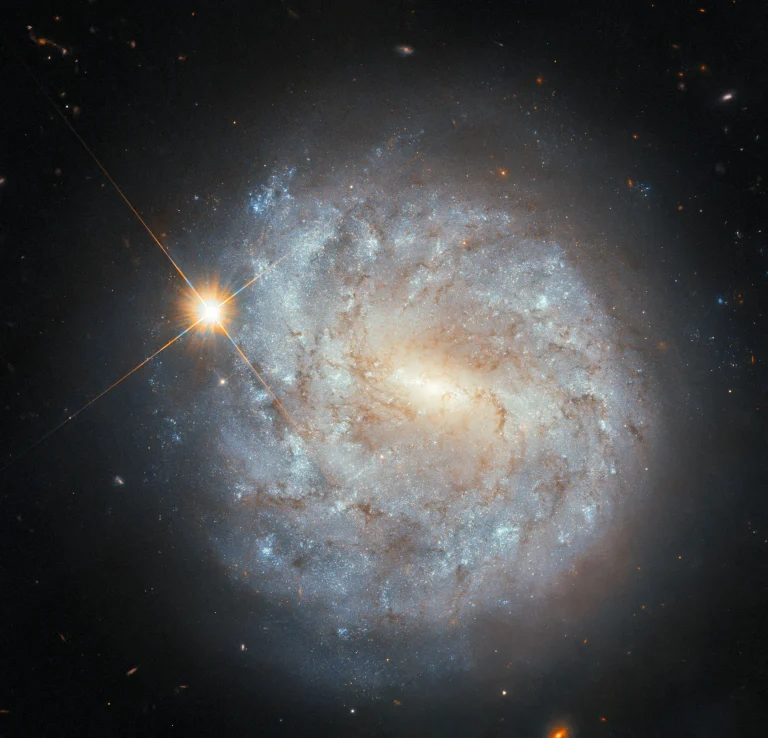
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope images showcases the galaxy NGC 2217.
ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Dalcanton; Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt (Geckzilla)
The magnificent central bar of NGC 2217 (also known as AM 0619-271) shines bright in the constellation of Canis Major (The Greater Dog), in this image taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Roughly 65 million light-years from Earth, this barred spiral galaxy is a similar size to our Milky Way at 100,000 light-years across. Many stars are concentrated in its central region forming the luminous bar, surrounded by a set of tightly wound spiral arms.
The central bar in these types of galaxies plays an important role in their evolution, helping to funnel gas from the disk into the middle of the galaxy. The transported gas and dust are then either formed into new stars or fed to the supermassive black hole at the galaxy’s center. Weighing from a few hundred to over a billion times the mass of our Sun, supermassive black holes are present in almost all large galaxies.
This image was colorized with data from the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System (Pan-STARRS).
Text credit: European Space Agency (ESA)
这张NASA/ESA哈勃太空望远镜的照片展示了NGC 2217星系。
ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Dalcanton; 致谢: Judy Schmidt (Geckzilla)
在这张由NASA/ESA哈勃太空望远镜拍摄的图像中,NGC 2217(也称为AM 0619-271)壮观的中心棒在大犬座中闪耀着明亮的光芒。这个棒旋星系距离地球大约6,500万光年,直径10万光年,与我们的银河系大小相似。许多恒星聚集在其中心区域,形成发光棒,被一组紧密缠绕的旋臂所包围。
这类星系的中央棒在它们的演化过程中扮演了重要的角色,帮助将气体从星系盘输送到星系中央。被输送的气体和尘埃要么形成新的恒星,要么被送入星系中心的超大质量黑洞。超大质量黑洞的质量是我们太阳的几百到十亿倍,几乎存在于所有的大星系中。
这张照片是用全景巡天望远镜和快速反应系统(Pan-STARRS)的数据着色。
文稿来源:欧洲航天局(ESA)