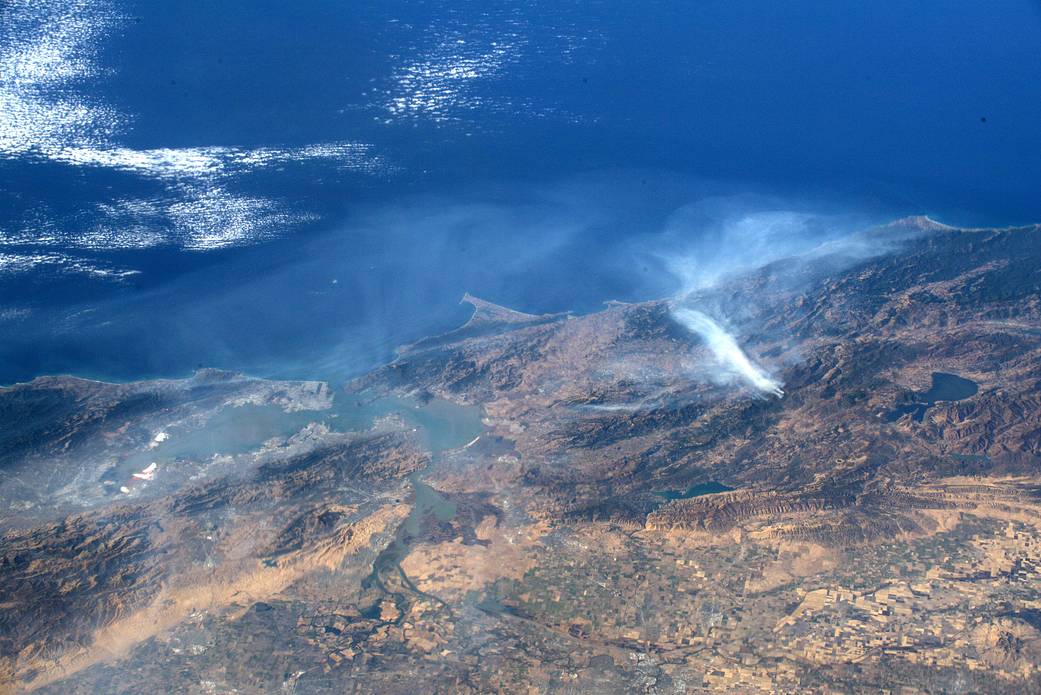
From the vantage point of space aboard the International Space Station, NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan captured this image of a California wildfire. On his Facebook page, he said: “From the International Space Station I was able to catch these pictures of the California wildfires burning north of the Bay Area. Thinking of the people who have lost their homes and the brave first responders on the front lines protecting them.”
In addition, NASA’s Earth-orbiting satellites are often the first to detect wildfires burning in remote regions, and the locations of new fires are sent directly to land managers worldwide within hours of the satellite overpass. Together, NASA instruments detect actively burning fires, track the transport of smoke from fires, provide information for fire management, and map the extent of changes to ecosystems, based on the extent and severity of burn scars. NASA has a fleet of Earth-observing instruments, many of which contribute to our understanding of fire in the Earth system. Satellites in orbit around the poles provide observations of the entire planet several times per day, whereas satellites in a geostationary orbit provide coarse-resolution imagery of fires, smoke and clouds every five to 15 minutes.
Learn more at www.nasa.gov/fires.
Image Credit: NASA
在国际空间站的有利位置,美国宇航局宇航员安德鲁·摩根拍摄了这张加利福尼亚野火的照片。在他的脸书主页上,他说:“我从国际空间站上拍到了这些加州野火在海湾地区北部燃烧的照片。想想那些失去家园的人们,想想保护他们的勇敢的前线急救人员。”
此外,美国宇航局的地球轨道卫星常常是第一个探测到偏远地区发生火灾的卫星,新火灾的地点在卫星立交桥数小时内就会直接发送给世界各地的土地管理者。与此同时,NASA的仪器可以探测到正在燃烧的火灾,跟踪火灾产生的烟雾的传播,为火灾管理提供信息,并根据烧伤的范围和严重程度绘制生态系统变化的程度图。美国国家航空航天局拥有一批地球观测仪器,其中许多有助于我们了解地球系统中的火。在极地轨道上的艾略特卫星每天可以对整个行星进行几次观测,而在地球静止轨道上的卫星每5到15分钟就可以对火、烟和云进行一次粗略分辨率的观测。
更多信息请访问www.nasa.gov/fires。
图片来源:NASA