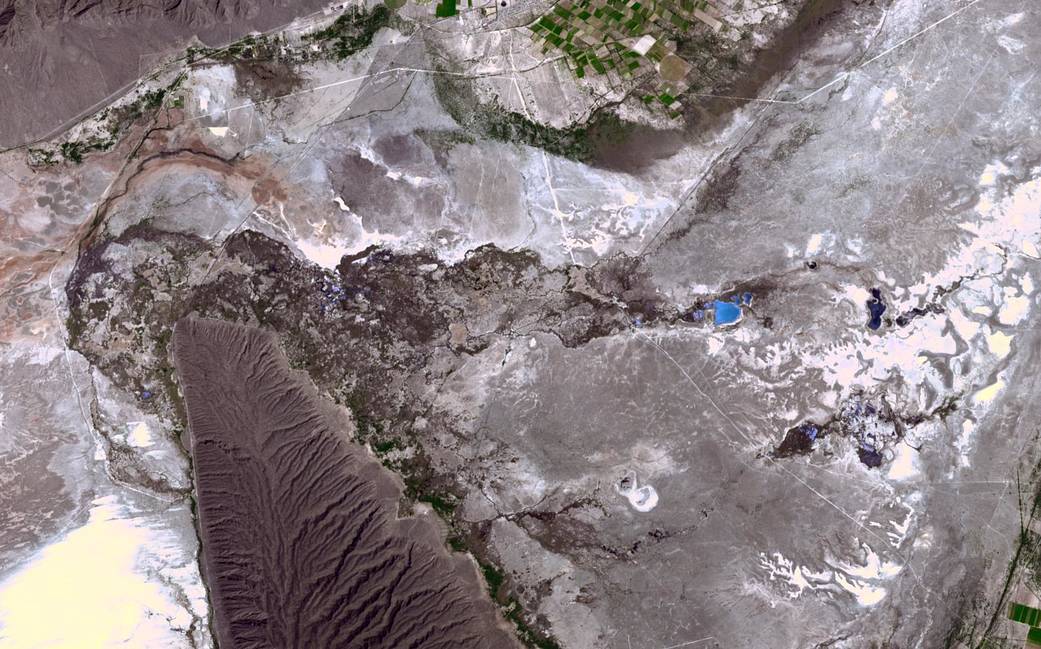
In the northern Mexican state of Cohuilla lies the Cuatro Cienegas Basin. Dotting the landscape are small pools, formed by natural springs, in which are found live stromatolites. These stony layered structures are formed by colonies of cyanobacteria that trap sedimentary grains. Their major presence in the fossil record of several billion years ago is evidence of some of the earliest life on Earth. The biological reserve of Cuatro Ciénegas could have strong links to discovering life on Mars, since the adaptability of bioforms in the region is unique in the world.
The image was acquired April 1, 2017, covers an area of 14.9 by 23.8 km, and is located at 26.9 degrees north, 102.1 degrees west by the ASTER instrument aboard the Terra satellite.
With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of about 50 to 300 feet, ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance.
Image Credit: NASA/METI/AIST/Japan Space Systems, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team
Cuatro Cienegas盆地位于墨西哥北部的科韦拉州。点缀风景的是由天然泉水形成的小池塘,里面有活的叠层石。这些石质层结构是由聚集在沉积颗粒中的蓝藻菌群形成的。它们主要存在于数十亿年前的化石记录中,是地球上一些最早生命存在的证据。Cuatro Cienegas的生物保护区可能与发现火星上的生命有很强的联系,因为该地区生物形态的适应性在世界上是独一无二的。
这幅图像是在2017年4月1日拍摄的,覆盖面积14.9×23.8公里,由Terra卫星上的ASTER仪器测量,位于北纬26.9度,西经102.1度。
ASTER拥有从可见光到热红外波段的14个光谱波段,以及大约50至300英尺的高空间分辨率,能够为地球绘制地图并监测地球表面的变化。ASTER是1999年12月18日在地球上发射的5个地球观测仪器之一。ASTER的广谱覆盖和高光谱分辨率为众多学科的科学家提供了地表测绘和动态条件和时间变化监测的关键信息。应用实例是监测冰川的前进和后退;监测潜在的活火山;识别作物压力;确定云的形态和物理性质;湿地评价;热污染监测;珊瑚礁退化;土壤和地质的表面温度制图;测量表面热平衡。
图片来源:NASA/METI/AIST/Japan Space Systems, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team