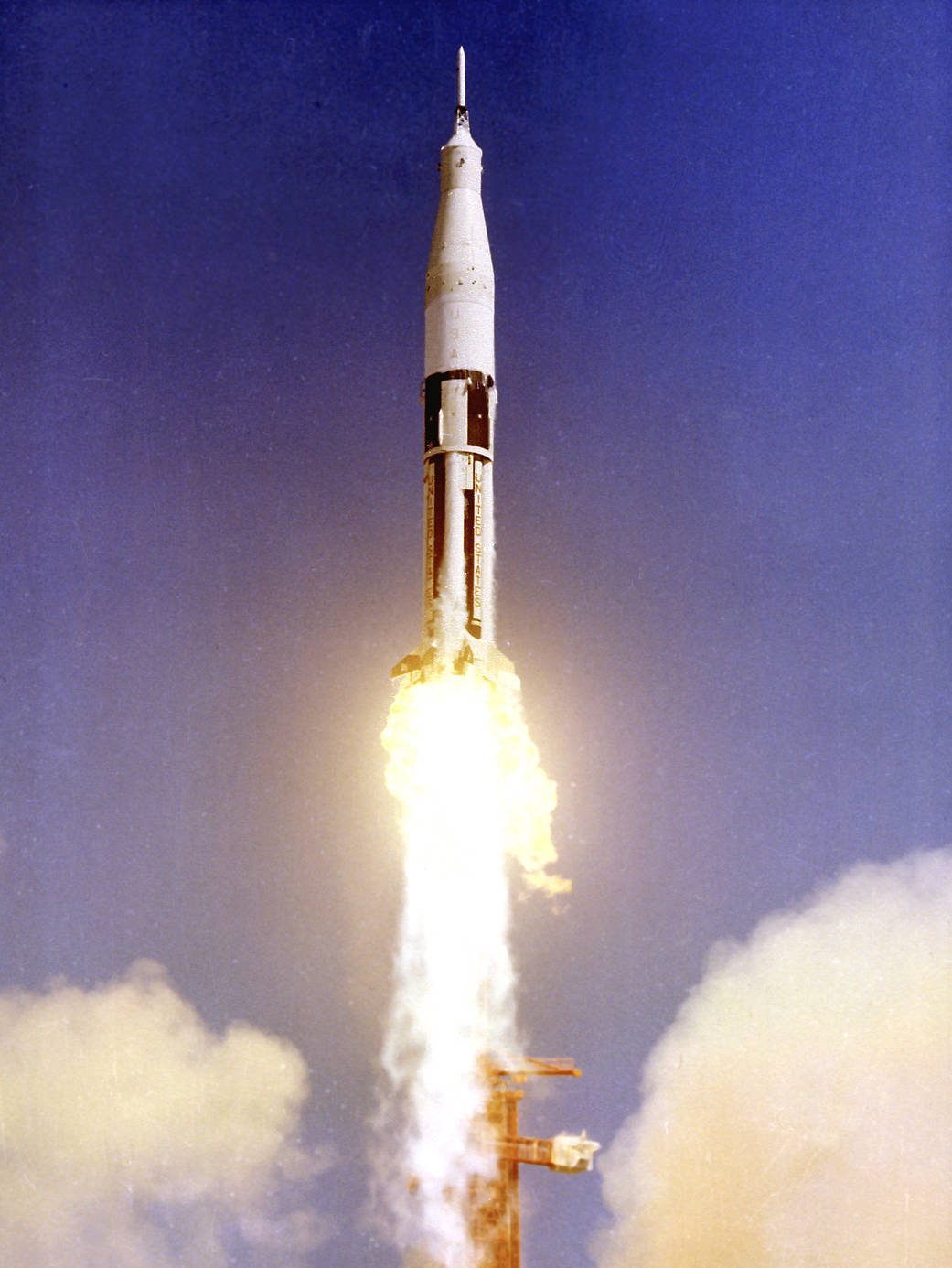
On Feb. 26, 1966, AS-201, the first Saturn IB rocket, lifted off from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Designed and developed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, the AS-201 mission was an uncrewed suborbital flight to test the Saturn IB and the Apollo Command and Service modules. The objectives of the flight were to verify the structural integrity, launch loads, stage separation and operation of subsystems of the Saturn 1B, and evaluate the Apollo spacecraft subsystems, heatshield and mission support facilities.
Today, NASA aims to return to the Moon by 2024 with our Artemis Program, which will land American astronauts, including the first woman and the next man, on the Moon. Through the agency’s Artemis lunar exploration program, we will use innovative new technologies and systems to explore more of the Moon than ever before. We will collaborate with our commercial and international partners to establish sustainable missions by 2028. And then we will use what we learn on and around the Moon to take the next giant leap – sending astronauts to Mars.
Image Credit: NASA
1966年2月26日,第一枚土星IB火箭AS-201从美国宇航局肯尼迪航天中心发射升空。由美国国家航空航天局马歇尔太空飞行中心设计和开发的AS-201任务是一次无人驾驶亚轨道飞行,以测试土星IB和阿波罗指挥和服务模块。此次飞行的目的是验证土星1B的结构完整性、发射载荷、阶段分离和子系统的操作,并评估阿波罗飞船的子系统、隔热板和任务支持设施。
今天,美国国家航空航天局计划在2024年通过我们的阿尔特弥斯计划重返月球,该计划将使美国宇航员,包括第一位女性和第二位男性,登上月球。通过该机构的阿尔特弥斯月球探索计划,我们将使用创新的新技术和系统来探索比以往任何时候都更多的月球。我们将与我们的商业和国际伙伴合作,在2028年前建立可持续的任务。然后,我们将利用我们在月球上和月球周围学到的知识,进行下一个巨大的飞跃——把宇航员送上火星。
图片来源:NASA